Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh
Scottish Stroke Collaboration Meeting
22nd September 2010
Queen Mother Conference Centre
The Hyperacute Stroke Unit
Model NHS Ayrshire & Arran
BACKGROUND 2008
• NHS Ayrshire & Arran offers a comprehensive
stroke care service.
• In Ayr hospital - 15 acute stroke beds in 30
bedded acute geriatric assessment unit. 20
rehabilitation beds at different site.
• In Crosshouse hospital – 21 acute stroke beds in
acute geriatric assessment unit. 20 rehabilitation
beds at different site.
QIS Standards 2008
• 70% of stroke patients are admitted within 1 day
of admission.
• Swallowing assessment 100% on day of
admission.
• CT scan 80% within 2 days of admission.
• Aspirin – 100% of definite ischaemic events
within 2 days of admission.
Ayr Hospital 2008 figures
• 71% entered stroke unit within 1 day.
• Swallowing assessment 64%.
• 74% of patients scanned within 2 days of
admission.
• Aspirin 49% within 1 day.
Background of Hyperacute stroke
unit (HASU)
• Agreed all possible stroke patients should be
admitted to a designated area with specialised
medical & nursing input.
• It would enhance implementation of QIS
standards.
• Facilitate monitoring of patients with a proposed
limited thrombolysis service.
Design of HASU
• 6 bedded mixed sex area in 30 bedded acute
geriatric assessment unit.
• Changed 15 stroke beds to 6 HASU beds & 9
acute stroke beds.
• 1 registered nurse & 1 NA allocated 24/ 7 plus
an additional registered nurse Mon - Fri 0830 1630.
• Daily medical review followed by brief review of
investigation on same day.
Design of HASU
• Close monitoring of occupancy with
agreed protocol of transferring patients out
of HASU.
• Priority of at least 1 HASU bed 24/7 for
proposed thrombolysis.
• Continuous monitoring of all patients
including thrombolysis patients.
• Additional training for nurses.
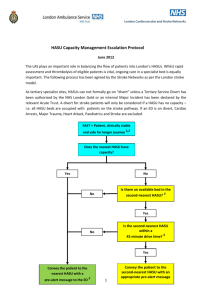
Patients journey
Patients with possible TIA / Stroke
Admission to HASU
immediate HASU
nurse review including NIHSS
medical
review non-stroke diagnosed - moved out
of HASU
Stroke diagnosed – stroke
protocol initiated.
Period review
• 01-04-08 – 31-03-09 pre- HASU
• 01-04-09 – 31-03-10 post- HASU
Number of patients
Pre - HASU
419
Post HASU
527
Number of admissions
Pre HASU
Post HASU
419
527
Number of stroke
patients
Number of stroke
patients
377
403
Comparison of QIS data
pre & post HASU
QIS Standard
PRE
POST
2008 - 70% enter stroke unit within 1 day.
2009 - 90% by 1 day
71%
92%
Swallowing 100% on day of admission
64%
82%
2008 - 80% scanned within 2 days of
admission. 2009- 80% on day of admission
26%- 37% 74% 82%
Aspirin 2008 – within 2 days of admission.
2009-100% on day of admission
49%
72%
Length of stay (days)
12.5
8
Number of deaths
27pts 23 pts
Number of patients discharged from ASU
24%
31%
Benefits
• Allows comprehensive assessment of patients
presenting with possible diagnosis of stroke/ TIA.
• Facilitates implementation of QIS Standards.
• Earlier detection of complications.
• Reduces length of stay in hospital.
• Safer environment for monitoring stroke patients
including those receiving thrombolysis.
• Increased motivation of staff in area.
• All new stroke patients clearly identified in HASU.
Challenges
• Increasing turn over of patients through a very
specialised area.
• Allows many non-stroke patients to be admitted to
HASU.
• Requires constant vigilance on bed management.
• Requires dedicated nurses with specialist knowledge in
stroke.
• Requires protected job plan for regular medical
supervision at a senior level.
• May have impact on AHP workload.
Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh
Scottish Stroke Collaboration Meeting
22nd September 2010
Queen Mother Conference Centre