CT_Scanner_development_March 2010_3_
advertisement

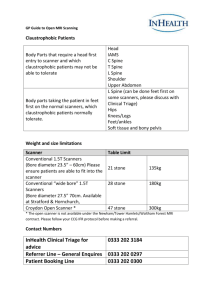
Development of the Computed Tomography (CT) Scanner Sue Edyvean St. George’s Hospital, London Development of CT Computed Tomography • Images ‘slices’ through the patient – ‘Graphia’ – to write, to draw – ‘Tomos’ – cut, incision, section – ‘Computed’ – determined by mathematical methods Development of CT Development of the CT Scanner • CT scanner developed at EMI Medical by Godfrey Hounsfield Development of CT Development of the CT Scanner • Prototype installed at Atkinson Morley’s Hospital, Wimbledon, London Development of CT Development of the CT Scanner • Support of Dr James Ambrose, Neuro-radiologist AMH Godfrey Hounsfield, James Ambrose Development of CT Development of the CT Scanner • 1st clinical scan 1st October 1971 Development of CT British Journal of Radiology 1973 – three linked papers • Godfrey Hounsfield – EMI, inventor of clinical CT 1971 (design) – 1979 Nobel prize (jointly with Cormack) • Dr. James Ambrose – Neuroradiologist AMH (clinical) – Standing ovation at RSNA 1972 • Dr. BJ Perry – Head of Medical Physics SGH/AMH (radiation) – Dosimetry and image quality, measurements and methods Godfrey Hounsfield Development of CT James Ambrose John Perry (GH died Aug 12th 2004, JA died March 12th 2006) CT scanner development 1971 • 2 x (8 – 10 mm), first dual slice scanner, • 80 x 80 matrix • 4 min per rotation Development of CT Early Clinical Images - AMH Scanner • Data tapes sent away overnight for image reconstruction • Paper (CT numbers) or polaroid (Scan numbers 200 and 215, images A and B refer to the two slices imaged simultaneously) Development of CT CT scanner development 1971 • Scanner is now in the science museum Development of CT Godfrey Hounsfield – Nobel Speech 1979 Fig. 14 shows a picture from the experiment. The heart chambers can be discerned by a little intravenous injected contrast media. A further promising field may be the detection of the coronary arteries. …. It may be possible to detect these under special conditions of scanning. Development of CT 2010 Scanning the heart has become a reality SOMATOM Definition Flash Temp res. 75 ms Coll. 128 x 0.6 mm Spatial res. 0.33 mm 350 ms for 149 mm Rotation 0.28 s 100 kV, 290 mAs/ rotation 0.90 mSv Development of CT Development of the CT Scanner Development of CT