Risk Management

Definition
Hazard - Anything, any source or any situation with the potential to cause bodily injury or ill-health
Risk – the likelihood that a hazard will cause a specific bodily injury to any person
Definition
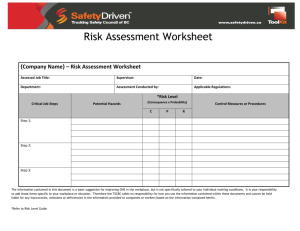
Risk assessment - The process of evaluating the probability and consequences of injury or illness arising from exposure to an identified hazard, and determining the appropriate measures for risk control.
Risk management - The identification, assessment and prioritisation of WSH risks followed by the application of control measures to minimise the probability and/or impact of undesirable WSH consequences.
Overview of Risk Management Process
Formation of Risk Management/
Risk Assessment Teams
RA Teams should have representatives from both the management and non-management levels.
The RA team should include personnel who are involved with the work, including contractors and suppliers who are experienced with the work involved.
Team Leader shall be competent for the task before leading the RA team and has attended a RM course conducted by a MOM Approved Training Provider
Gather Relevant Information
Workplace layout plan
Process or work flowchart
List of work activities in the process
List of chemicals, machinery and/ or tools used
Records of past incidents and accidents
Relevant legislation, CPs or specifications
Observations and interviews
WSH Inspection records
Details of existing risk controls
Health and safety audit reports
Feedback from employees, clients, suppliers or other stakeholders
SWPs
Other information such as safety data sheets (SDS), manufacturer’s instruction manual
Copies of any relevant previous RAs
Medical condition (e.g., allergy) of workers in the workplace or activity being assessed
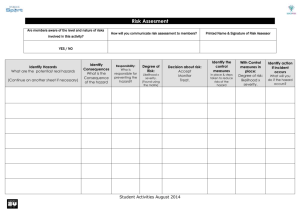
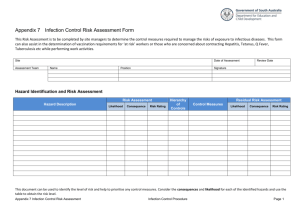
Identification of Hazards
Example:
Person falling from height
Object falling from height
Slips or falls on the level
Electrocution
Drowning
Noise induced deafness
Fire and explosion
Struck by or against object
Risk Evaluation
Risk has 2 parts:
Expected Severity of the hazard
Likelihood of the occurrence of the accident/incident or ill health
Severity is the degree or extent of injury or harm caused by accidents/incidents arising from workplace hazards
Using a 5X5 Risk Matrix
Severity Categories and Description for 5X5 Risk Matrix
Likelihood
Likelihood Categories and Description for 5X5
Risk Matrix
3x3 Risk Matrix to Determine Risk Level
Using a 5X5 Risk Matrix
5X5 Risk Matrix with Numeric Ratings to Determine Risk
Level
Hierarchy of Controls
Communication of Risk Management
Every employer, self-employed person and principal (including contractor and sub-contractor) must take all reasonably practicable steps to inform his employees or any other persons at the workplace who may be exposed to safety and health risk.
They should be informed of the following:
• the nature of the risk involved,
• the measures implemented to control the risk,
• applicable safe work procedures.
Whenever the risk assessment is revised, or when there is a significant change in work practices or procedures, the employees or other persons who may be at risk must be informed accordingly.
Review Effectiveness of Control Measure
Regular review of RA plan is critical
The RM Team should perform the steps (Hazard Identification,
Risk Evaluation and Risk Control) when conducting RA Review
Regular Auditing is required to ensure Risk Control measures have been implemented and are functioning effectively
While employers are required to review their plans every three years, a review should take place whenever:
1.
2.
3.
There are changes to the area of work
New information on safety and health risks surfaces
After any accident/incident