Visual pathways PP
advertisement

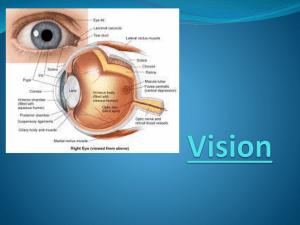
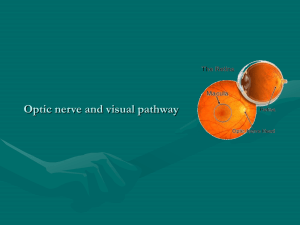
Visual Pathways Eye • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Lens Cornea Iris Suspensory ligaments Ciliary body Ciliary muscle Retina Choroid Sclera Subarachnoid space Central retinal artery and vein Optic nerve Vitreous body Conjunctiva Retina - contains • Pigment epithelial cells- absorb light that passes through the retina • First neuron • Rods- vision in light of low intensity • Cones- visual acuity and color vision • Second neuron • Bipolar- second neurons of visual pathway • Ganglion • Ganglion- third neurons of visual pathway Neuroanatomy OC TH 5090/PH TH 7050 - K. Bo Foreman PT, PhD Additional areas: • Optic disc- Area optic nerve exits retina (blind spot- no receptors) • Macula lutea- central region of the retina • Fovea centralis- area of the central part of the retina that is indented and contains mainly cones for visual acuity Visual Pathway• Light travels through retina from internal to external exciting the rods and cones • Impulse is transferred from rods and cones to bipolar cells • Bipolar cells synapse on the dendrites of the ganglion cells Neuroanatomy OC TH 5090/PH TH 7050 - K. Bo Foreman PT, PhD Visual Pathway• Ganglion cells form the optic nerve at the level of the optic disc • Optic nerves combine to form optic chiasm • Enters lateral geniculate body to synapse Visual Pathway- forth order neurons • Cell body located in the lateral geniculate body • Axon travels posteriorly (optic radiations) • Terminates in the visual cortex in the occipital lobe 1. 1. Right eye blindness - trauma, optic neuritis 2. 2. Bitemporal hemianopsia - pituitary tumors 3. 3. Right nasal hemianopsia - pressure by aneurysm of internal carotid artery 4. 4. Left homonymous hemianopsia - abscess or tumor of temporal lobe 5. 5. Left homonymous hemianopsia - anterior choroidal artery dysfunction 6. 6. Left homonymous superior quadratic anopsia - temporal or occipital lobe dysfunction 7. 7. Left homonymous inferior quadratic anopsia - parietal or occipital lobe tumor 8. 8. Left homonymous hemianopsia with macular preservation - posterior cerebral artery dysfunctions, tumors, trauma 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Neuroanatomy OC TH 5090/PH TH 7050 - K. Bo Foreman PT, PhD Lecture 14 - Visual Visual Reflexes • Light reflex (constriction- parasympathetic): when light enters the pupil the pupil constricts • Neuronal elements of the retina • Optic nerve • Optic chiasm • Optic tract • Enter the brachium of the superior colliculus (superior brachium) • Pretectal region • Oculomotor nuclear complex (Edinger-Westphal nucleus) • Preganglionic parasympathetic axons to the ciliary ganglion behind eye • Short ciliary nerves • Terminate on the constrictor muscle of the iris Neuroanatomy OC TH 5090/PH TH 7050 - K. Bo Foreman PT, PhD Lecture 14 - Visual Visual Reflexes • Light reflex (dilation- sympathetic): when the pupil widens. Occurs passively when parasympathetic tone decreases and actively when sympathetic tone increases • Hypothalamus • Spinal cord (T1) • Ventral root • White communicating rami • Ascend sympathetic trunk • Synapse in superior cervical ganglion with post-synaptic sympathetic ganglion • Travel in the carotid plexus • Terminate on the dilator muscle of the iris Neuroanatomy OC TH 5090/PH TH 7050 - K. Bo Foreman PT, PhD Visual Reflexes • Accommodation reflex: Process in which a clear visual image is maintained as gaze is shifted from a distant to a near point • 3 components • Convergence of the eyes • Pupillary constriction • Thickening of the lens • Initiated by occipital cortex • Impulses go to: • Edinger-Westphal nucleus for changes in the lens and pupil (parasympathetic) • Somatic nuclei: for convergence of the eyes (medial rectus Neuroanatomy OC TH 5090/PH TH 7050 - K. Bo Foreman PT, PhD