Sequence of Disabilities
advertisement
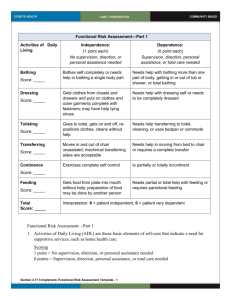
Sequence of Disabilities Network Analysis Presented by Farrokh Alemi, Ph.D. Research conducted by Cari Levy M.D., Manaf Zargoush Ph.D., Raya E. Kheirbek M.D., Allison E. Williams Ph.D., Arthur R. Williams Ph.D., Janusz Wojtusiak Ph.D., Bryce Sutton Ph.D., Etienne Pracht Ph.D., Bruce Citron Ph.D., Lisa Argyros and Phan Giang Ph.D. We Agree Causal Network Models: Association, Sequence, Counterfactual, Mechanism Causal Network Models: Association, Sequence, Counterfactual, Mechanism Sequence of disabilities has been the focus of cultural and scientific inquiries “His acts being seven ages … The sixth age shifts into the lean and slippered pantaloon, with spectacles on nose and pouch on side; his youthful hose, well saved, a world too wide for his shrunk shank; and his big manly voice, turning again toward childish treble, pipes and whistles in his sound. Last scene of all, that ends this strange eventful history, is second childishness and mere oblivion, sans teeth, sans eyes, sans taste, sans everything.” Shakespeare: As You Like It: Act 2, Scene 7, Page 6 5 6 7 1963 50 Bathing Walking Dressing Transfer Toileting Katz, Ford, Moskowitz, Jackson, & Jaffe Feeding 1997 Bathing Walking Dressing Transfer Toileting Dunlop, Hughes, & Manheim Feeding 1998 Bathing Walking Dressing Transfer Toileting Spector & Fleishman Feeding 1998 Bathing Walking Dressing Transfer Toileting Ferrucci, Guralnik, Cecchi et al Feeding We excluded from this list cutting toenails, shopping, use of steps, heavy housework, cooking hot meal, moving around outside, washing arms/face and light housework which were not studied across studies. Bathing includes showering or full wash and not simply face wash. 2001 Bathing Walking Dressing Transfer Toileting Jagger, Arthur, Spiers, Clarke Transferring refers to transfer from bed and not simply transfer from chair or toilet Feeding 2012 Bathing Walking Dressing Transfer Toileting Kingston, Collerton, Davies et al. Feeding Transferring refers to transfer from bed and not simply transfer from chair or toilet. Toileting includes transfer from toilet. Gill & Kurland 2003 A Multiple Path Network Model Is Needed 296,051 Residents Admissions 1,820,714 Assessments 79.88% White, 96.34% Men, 74.36 years (SD=11.44) Old at 1st Assessment Too Much All Data 25 Combinations 84% of All Cases B=Bathe, W=Walk, G=Groom, D=Dress, T=Toilet B=Bathe, W=Walk, G=Groom, D=Dress, T=Toilet, L=Bowel Continence, S=Transfer, U=Urinary Continence and F=Feeding disabilities Trimmed Mean Days to Partial Recovery of One Disability Insurance Still Too Confusing Statistical Summary Learn New Network Model Relationship of 9 Disabilities Nodes Are Connected Based on Associations Direction is Set Based on Independence Structure Algorithms for Learning Network Models Cross Section Analysis Longitudinal Analysis Algorithms for Dynamic Modeling: Confusing Network Model Do as Humans Do Learn Network Model Cross Section Analysis Longitudinal Analysis Subject to Longitudinal Constraints Probabilistic Contrast Do as Humans Do Numbers show the correlation between two disabilities. Dashed red arrows show the maximum likelihood path. Many Pathways from Start to End Numbers show the correlation between two disabilities. Dashed red arrows show the maximum likelihood path. Analytical Progress Use Longitudinal Constraints Clinical Relevance Experience of Majority Policy Implications Don’t Give Up at 100 Days