toepler
advertisement
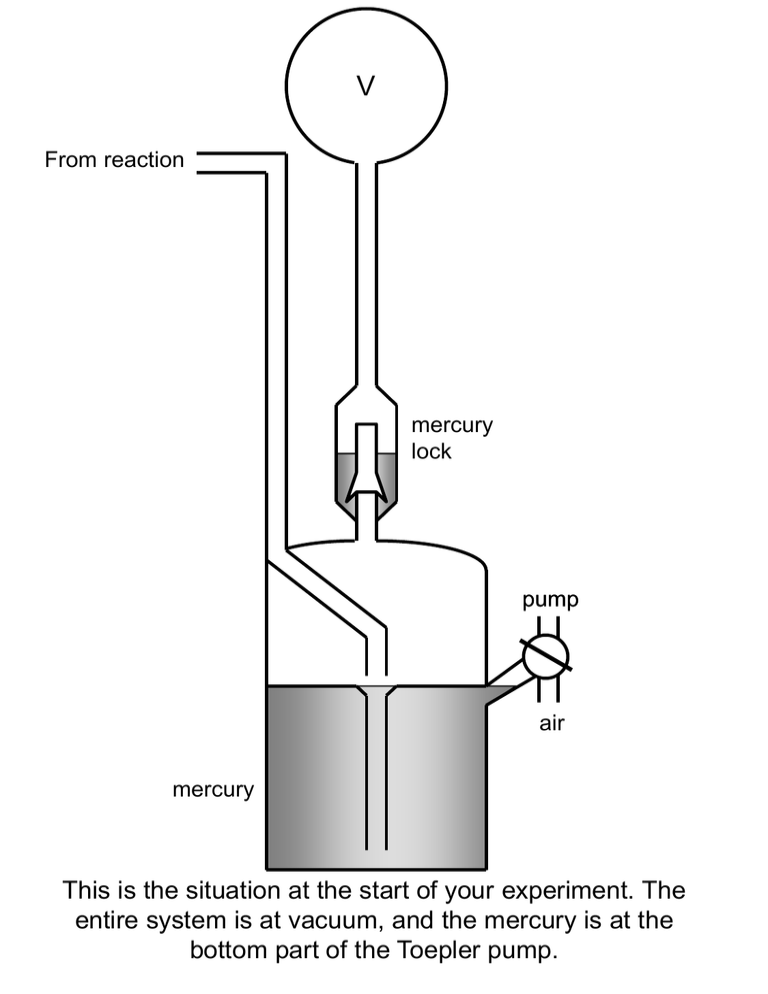
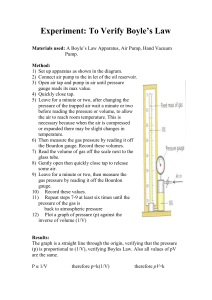
V From reaction mercury lock pump air mercury This is the situation at the start of your experiment. The entire system is at vacuum, and the mercury is at the bottom part of the Toepler pump. V pump The valve at the right-hand side is directed to the pump to retain the mercury at the bottom part. V pump After opening the reaction vessel, the gas formed in the reaction will enter the top part of the Toepler pump. V air By directing the valve to atmospheric pressure, the mercury will be pushed upwards, thus compressing the gas that was in the upper part. V air At a certain point, the compressed gas will be pushed through the mercury lock. V pump By directing the valve back to the pump again, the mercury will be transferred back to the bottom . V pump When the mercury is transferred back to the bottom part, the remaining gas will equilibrate. V air Now the cycle will be repeated. Compressing the gas V air Now the cycle will be repeated. Pushing the gas through the mercury lock V pump Now the cycle will be repeated. Transferring the mercury back to the bottom part. V pump Now the cycle will be repeated. Allowing the gas to equilibrate V pump At a certain point, all the gas is transferred into the calibrated volume. Now you can push the mercury upwards... V mark air …until the mark which indicates the limit of the calibrated volume is reached. V Dp air You can measure the pressure in the calibrated volume, by reading the difference in height in the two legs, and calculate the amount of gas.