RADIATION
advertisement

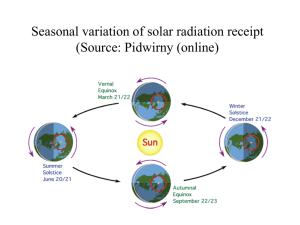
RADIATION Insolation intercepted solar radiation Earth intercepts 0.0000000005 of the sun’s radiation Solar constant amount of radiation received at the top of the atmosphere (on a plane surface perpendicular to sun’s rays) = 1372 Watts/m2 (reduced by half by the time it reaches surface of earth) energy per unit area amount of energy received at earth’s surface per unit of area (square meter, square inch, etc.) surface receives more energy per unit area (more concentrated) when the sun’s rays are vertical (direct) less energy per unit area (less concentrated) when sun’s rays are oblique (slanted) Electromagnetic Radiation • Radiant energy • Earth, sun, everything! radiates energy – tropical zones receive more energy than they radiate – polar zones radiate more energy than they receive – excess heat transfer: • ocean currents, winds • Sun’s energy from atomic fusion: hydrogen atoms fused into helium atoms – lost mass converted to energy • Electromagnetic radiation (EMR) – travels at speed of light (93 million miles in 8.5 minutes) – travels in waves Wavelength: size of wave electromagnetic spectrum • “ruler” to measure different types of energy Solar (Sun) vs. Terrestrial (Earth) Radiation: • sun’s SHORTWAVE : – gamma , X-ray, UV, visible, infrared • earth’s LONGWAVE : – infrared Absorption of radiation in the atmosphere: • Shortwave absorbers: • ozone, water vapor • Longwave absorbers: • water vapor, carbon dioxide, ozone • “The atmosphere is relatively transparent to shortwave radiation and opaque to longwave radiation” Types of heat energy • Sensible heat • thermometer • Latent heat • released or stored in a phase change • First Law of Thermodynamics: • energy cannot be created or destroyed, but can be: CONVERTED TRANSFERRED Energy Transfer Mechanisms: • Conduction • energy transmitted within a substance by collision of molecules • Convection • vertical motion of energy from one place to another through physical motion of air Energy Budget/Balance • Exchange of energy between the sun, the earth, and the atmosphere – balance between incoming and outgoing • radiation entering the atmosphere can be: • absorbed • transformed, re-emitted • reflected • “albedo” : percentage of incoming radiation that is reflected; • earth/atmosphere albedo = 31 % Incoming solar shortwave radiation Longwave exchanges between surface, atmosphere, and space: The Balancing Act • 95+48 = 143 • energy leaves surface as: – radiation – latent heat (evaporation) – sensible heat (conduction) • losses: 114+23+7= 144 Counterradiation by the atmosphere: Greenhouse Effect • atmosphere admits most shortwave; absorbs and counterradiates longwave • allows average surface temperature to be 59oF rather than - 4oF Review of energy balance Latitudinal differences in net radiation Seasonal and Diurnal (daily) differences in insolation Seasonal and Diurnal (daily) differences in net radiation