ch.2meteor

Disciplines of Science, ch. 16
The Atmosphere
Question of the Day
–What is the difference between weather and climate?
Elements of weather and climate
– Properties that are measured regularly
– Most important elements
• Temperature
• Humidity
• Cloudiness
• Precipitation
• Air Pressure
• Winds speed and direction
Atmosphere v What is the most abundant gas? least?
v Variable components of air
– ozone
– absorbs harmful UV radiation
– water vapor
– absorbs heat energy from Earth
– aerosols
– reflects sunlight
Atmospheric pressure variation with altitude
Figure 16.5
Layers of the Atmosphere v Based on temperature
– Troposphere
What happens to temp. as altitude increase
§ Environmental lapse rate
6.5˚C per kilometer (average)
3.5˚F per 1000 feet (average)
– Stratosphere
– Mesosphere
– Thermosphere
Earth-Sun relations v What is the difference between rotation and revolution in regards to the Earth?
– perihelion vs. aphelion v What causes seasons?
– Revolution of the earth around the sun
– Sun Angle
– directly overhead, solar radiation more concentrated
– determines the thickness of atmosphere to travel through
Relationship of sun angle and solar radiation received on
Earth
What do you think happens to solar radiation as the angle increases?
Calculating Noon Sun Angle
3 things to know:
– location, date, location of 90 0 Sun
Example
– Location: 40 0 N, Date: 12/22, location: 23.5
0 S
– Add both locations and subtract from 90
– 90-63.5= noon sun angle is 26.5
0
– Figure out Noon Sun Angle for 42 0 on 9/22.
Daily paths of the Sun at
40º N latitude
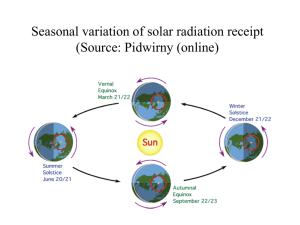
Seasons v Northern Hemisphere
• Summer solstice (june 21/22)
• Winter solstice (december 21/22)
• Autumnal equinox (september 22/23)
• Vernal (Spring) equinox (march 21/22) v Southern Hemisphere
– seasons are opposite that of the Northern
Hemisphere
Earth-Sun relationships
Figure 16.12
Characteristics of the solstices and equinoxes
Figure 16.13
Atmospheric heating v What is the difference between temperature and heat?
v Mechanisms of heat transfer
– Conduction
– What is the difference between a conductor and an insulator?
– Convection
– Radiation
Mechanisms of heat transfer
Figure 16.16
The electromagnetic spectrum
Figure 16.17
Atmospheric heating v Incoming solar radiation
– Atmospheric effects
• Reflection – albedo (percent reflected)
• Scattering
• Absorption
– About 50% absorbed at Earth's surface
Average distribution of incoming solar radiation
Figure 16.19
Atmospheric heating v Radiation from Earth's surface
– Longer wavelength terrestrial radiation is absorbed by
• Carbon dioxide
• Water vapor in the atmosphere
• Lower atmosphere is heated from Earth's surface
– Heating of the atmosphere is termed the greenhouse effect
The heating of the atmosphere
Figure 16.21