Warming and cooling the earth
advertisement

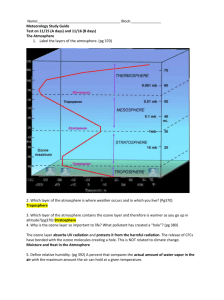
Warming/Cooling the Earth Warming - Incoming radiation absorbed by surface (most important) - Air molecules in direct contact w/ surface warm via conduction o Air near surface is very dense (a lot of molecules, draw vs. z), so warm molecules collide w/ other onesother molecules warmed - As air near surface warms, it becomes less dense than the air above it, so the warm air rises and the cold air sinks (convection) - Rising air will cool as it ascends upwards, and expand. (gas law) - air may condense (releasing latent heat) and may form cloud droplets - earth emits longwave radiation, but some LW radiation is absorbed by atmosphere (GH effect) and emitting back towards the surface o Most CO2 and H2O is relatively close to surface, so GH effect deals with atmosphere near surface Cooling - earth emits longwave radiation that escapes to space (most important) - only some LW radiation is absorbed by atmosphere (GH effect) and emitted back towards the surface - Evaporation and evaporative cooling o evaporative cooling: when rain evaporates it cools the surrounding air o wind increases evaporationcools