P1 1.1 1.2 Infrared Radiation
advertisement
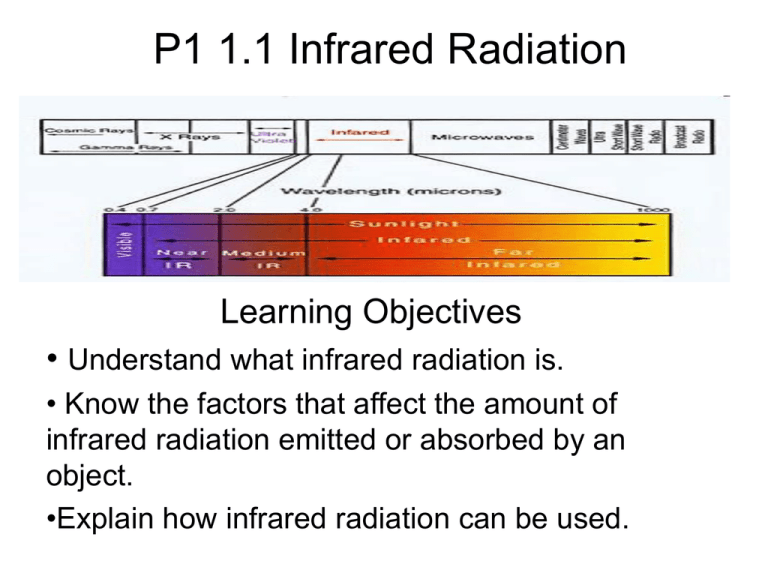
P1 1.1 Infrared Radiation Learning Objectives • Understand what infrared radiation is. • Know the factors that affect the amount of infrared radiation emitted or absorbed by an object. •Explain how infrared radiation can be used. Starter: Where and how is heat transfer taking place at this seaside? • Barbecue grill cooking burgers and sausages (conduction, radiation). • The car bonnet is so hot that as a sideline to the barbecue, someone is cooking food on it (conduction). • Picnic boxes labelled “cold” and “hot” contain items that have been kept cool and warm, respectively, to prevent heat transfer taking place. • The twins on the left are wearing identical clothing except that one is wearing a white t-shirt and keeping cool, while the other is wearing a black t-shirt and looking much hotter (radiation). • The twin in the black t-shirt is trying to keep himself cool with a portable fan (convection). • The fluttering sails on the boat out at sea and the fluttering flag on the flagpole show that it is windy at the seaside (convection). • The ice-creams are melted very quickly by the heat of the Sun, much to the annoyance of the child near the ice-cream van (radiation). What does this camera show? Transferring energy • If two objects are at different temperatures e will be transferred from the h to the cooler object, until they are both the s temperature. This can happen in different ways • Infrared radiation • Conduction • Convection Infrared radiation • Energy can travel through materials or through a vacuum as IR. IR transfers energy by waves. Infrared waves are similar to waves, except that we cannot see them. • Everything and absorbs IR. The amount of IR absorbed or emitted by a body depends on its temperature and the nature of its surface. Light, Emits, Electromagnetic, Transparent Emitting and absorbing infrared radiation. • Q) Design a table showing which items of the school uniform are good and bad in the summer and the winter, with reasons for this? • A surface will reflect some of the infrared radiation that reaches it, and absorb the rest. • Light coloured, shiny surfaces are good at reflecting radiation, so they are poor at absorbing it. Dark, matt surfaces are good at absorbing radiation. • Surfaces that are good at absorbing radiation are also good at emitting it. Dark matt surfaces are good emitters of radiation, and light shiny surfaces are poor emitters. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2--0q0XlQJ0 1. What is the image? 2. What is it? 3. It’s a zebra. But in visible light, what colour are the stripes that look white in infrared? 4. What is it? 5. Why would someone want an infrared image of their house? 6. Why does the lizard look so different in colour from the hand in this infrared picture? 7. Here you can see infrared waves doing something that all types of wave can do. What? Quick Quiz 1. Do all objects emit infrared radiation? 2. Cross out the incorrect words: The (hotter/cooler) an object is the (more/ less) infrared radiation it radiates in a given time. 3. What kind of surfaces are good emitters of infrared radiation? 4. What kind of surfaces are poor emitters of infrared radiation? Planning an experiment • Plan a class experiment to: “To measure the temperature of hot water cooling in shiny and dark cans”. – Discuss what the independent, dependent and controlled variables are. – What is the fair test for this investigation? – Make a prediction. – Draw a labelled diagram of your experiment. – Write a method to explain what you would do. – What would you expect to happen? – Design a results table. Copy and complete: • If two objects made from the same material have identical v_________, a thin, flat object will radiate heat energy faster than a f____ object. This is one reason why domestic radiators are t______ and flat. • Radiators are often painted with w_______ gloss paint. They would be better at radiating heat if they were painted with b______ matt paint, but in fact, despite their name, radiators transfer most of their heat to a room by c___________. Plenary • Explain why marathon runners are wrapped in foil blankets following a race. • Explain why kettles are light coloured.