Strategic group analysis
advertisement
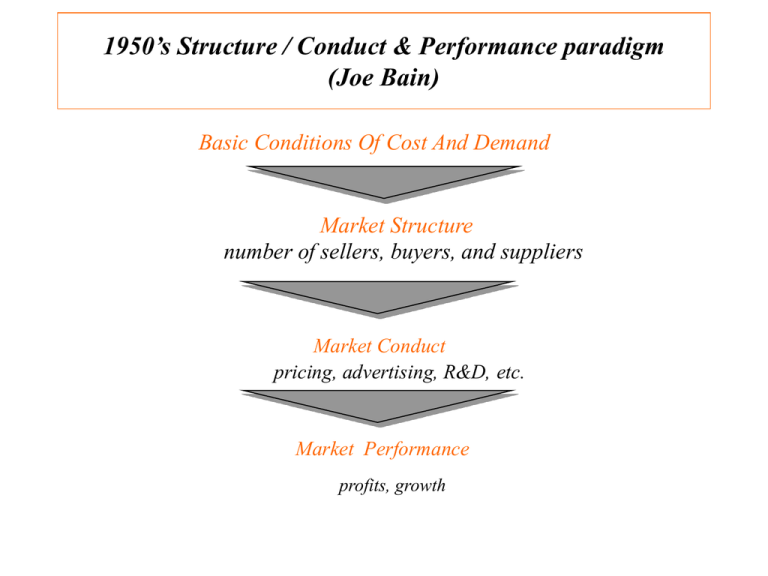
1950’s Structure / Conduct & Performance paradigm (Joe Bain) Basic Conditions Of Cost And Demand Market Structure number of sellers, buyers, and suppliers Market Conduct pricing, advertising, R&D, etc. Market Performance profits, growth Strategic Group Analysis “No two species that depend on the same prey will think differently” - Gause “Laws of natural competition” A strategic group is a group of firms in an industry following the same or similar strategy. Identifying strategic groups: • Identify principal strategic variables which distinguish firms. • Position each firm in relation to these variables. • Identify clusters of common competing characteristic Strategic Groups in the World Automobile Industry Broad GLOBAL, BROAD-LINE PRODUCERS e.g., GM, Ford, Toyota, Nissan, Honda, VW REGIONALLY FOCUSED BROAD-LINE PRODUCERS e.g. Fiat, PSA, Renault, Rover, Chrysler Product Range GLOBAL SUPPLIERS OF NARROW MODEL RANGE e.g., Volvo, Subaru, Isuzu, Suzuki, Saab, Hyundai NATIONALLY FOCUSED, INTERMEDIATE LINE PRODUCERS e.g. Tofas, Kia, VAZ, Maruti NATIONALLY- FOCUSED, SMALL, SPECIALIST PRODUCERS e.g., Bristol (U.K.), Classic Roadsters (U.S.), Morgan (U.K.) Narrow National LUXURY CAR MANUFACTURERS e.g., Jaguar, Rolls Royce, Daimler-Benz, BMW PERFORMANCE CAR PRODUCERS e.g., Porsche, Maserati, Lotus Geographical Scope Global A Framework for Competitor Analysis OBJECTIVES • What are competitors current goals? • Is performance meeting there goals? • How are its goals likely to change? STRATEGY • How is the firm competing? ASSUMPTIONS • What assumptions does the competitor hold about the industry and itself? RESOURCES & CAPABILITIES • What are the competitors’ key strengths and weaknesses? PREDICTIONS • What strategy changes will the competitor initiate? • How will the competitor respond to our strategic initiatives? Tool: CCSI (Core Competency Strategic Intent matrix Matrix) • The CCSI matrix makes firm dynamics alive. • Matrices are made at regular intervals – Yearly or quarterly depending on how fast things are changing • The two dimensions of the matrix are: – Core Competency: firms’ relative capacity -- as measured by Tobin’s Q or market/book value or defect rates(Customer switching) or as rated by industry experts. – Strategic Intent: firms’ relative aggressiveness -- as measured by R&D expenditures or capital investments or analysis of press releases. Tool: CCSI Matrix Average Low Core Capabilities High Each competitor is mapped as a circle: • the size of which reflects sales or capitalization or assets • and the pie slice in which reflects free cash or other available resources Passiv e Average Strategic Intent Aggressiv e Case: CCSI Analysis of the early 90s Automobile Industry • Flip & Observe ; – – – – The decline of Honda & Toyota The ascendancy of Ford General Motors unsuccessful run at leadership Chrysler’s repositioning as an up and coming star. High Automobile Industry 1990 1.5 illustrative Toyot a Honda .5 General Motors Chrysle r Ford (.50 ) (1.0) (1.5) Low Core Capabilities 1.0 .88 Passiv e .92 .96 1.04 Strategic Intent 1.08 1.12 Aggressiv e Automobile Industry 1991 illustrative High Toyot a 1.5 Honda .5 Chrysle r (.50 ) Ford (1.0) General Motors (1.5) Low Core Capabilities 1.0 .88 Passiv e .92 .96 1.04 Strategic Intent 1.08 1.12 Aggressiv e High Automobile Industry 1992 illustrative Toyot Honda a 1.5 .5 Ford General Motors (.50 ) Chrysle r (1.0) (1.5) Low Core Capabilities 1.0 .88 Passiv e .92 .96 1.04 Strategic Intent 1.08 1.12 Aggressiv e End of Deck