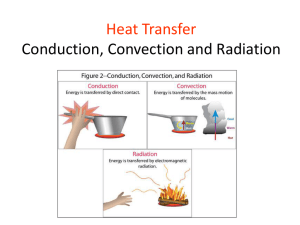
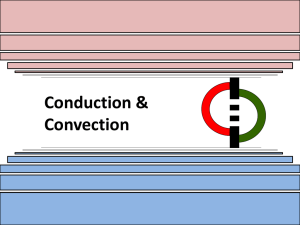
Conduction
advertisement

Chapter 8 – Energy Transfer and Conservation Introduction What does “transfer” mean? Movement of energy from one place to another without a change in form What does “transformation” mean? Process changing from one form of energy to another Are they the same thing? KEY QUESTION How does the transfer of energy affect natural and human-built environment? Natural vs. Human-Built How do natural environments differ from human-built environments? Natural environments are living and non-living things that occur naturally; human-built environments have been invented and built by people Natural and Human-Made What are some examples of things and processes that occur in our natural environment? Oceans, mountains, the wind, water, sunlight, etc. What are some examples of things and processes that that are human-built? Bridges, cars, coffee cups, etc. 8.1 Thermal Energy Transfer What is the definition of thermal energy? Thermal Energy: the total kinetic energy and energy of attraction of all the particles of a material we can increase the thermal energy of a substance by heating it We can decrease the thermal energy of a substance by cooling it Changes in thermal energy can cause a substance to change states (solid to liquid, etc.) What if…? What would life be like if we didn’t have refrigerators, air conditioners, and heaters? Read page 203 8.3 Conduction Figure 1 on page 206 What is happening? Explain. Conduction Conduction: the transfer of thermal energy through a substance, or between substances in contact, by the collision of particles Particles must collide in order for thermal energy to be transferred by conduction Question… Can conduction occur between two objects that are not touching or connected in some way? No…conduction can only occur between two objects or substances that are touching. Read page 206 and 207 8.4 Conduction and Geological Processes Trivia: What is the Earth made up of? The mantle is almost entirely solid rock. It contains a small amount of molten rock, but the vast majority is solid. What does “geological” mean? Having to do with the Earth and rocks How might conduction effect geological processes? Geothermal Energy Geothermal Energy: is energy contained below the Earth’s surface Read top of page 208 Volcanic Eruptions The volcanic eruptions that cause hot magma to be pushed to Earth’s surface are not caused by conduction; the magma rises toward the surface because it is less dense than the surrounding rock. Magma is often under pressure because it is in tight spaces when it is heated. Magma and lava lose a lot of thermal energy through conduction into the surrounding rocks or air. Heat and Rock Formation Igneous rock: rock formed from magma that has cooled and solidified Metamorphic rock: rock that is formed when heat and pressure change existing rock Heat and Rock Formation Once the rock is exposed to high temperature and pressure, thermal energy is transferred to the rock by conduction This causes the particles of the rock to be rearranged, resulting in the formation of metamorphic rock, including diamonds Diamonds Form deep in the Earth’s crust Heat and pressure may change substances into diamond Metamorphic rock 8.5 Convection Convection: the transfer of thermal energy from one part of a fluid to another by circulating current of faster-moving and slower-moving particles Convection occurs in a fluid whenever warmer fluid exists below cooler fluid. Heating fluid from below causes convection because it produces an area of warm fluid at the nottom of an area of cooler fluid. Steps to heating a pot of soup on the stove… Groups of 3 or 4 Arrange the steps in the correct order Figure 1 on page 210… What is happening when this pot of soup is heated? Read page 210 and 211 8.6 Convection in the Environment What did you notice during the last thunderstorm we had/you remember? What were the conditions before the storm? Why do thunderstorms happen? Occur largely because of the effects of convection in the atmosphere Change in temperatures What is convection and conduction? Convection: the transfer of thermal energy from one part of a fluid to another by circulating current of faster-moving and slower-moving particles Conduction: the transfer of thermal energy through a substance, or between substances in contact, by the collision of particles Thunderstorms Thunder and lightening Can lead to hail, tornados, and hurricanes The Earth’s surface is heated by the sun Energy is transferred to the air by conduction The warm air is pushed up higher Large puffy clouds appear A lot of thermal energy released Read top of page 213 8.7 Radiation What is our major source of energy? The Sun Conduction and convection can only occur when matter is present In this section, we will learn about the third type of energy transfer that does not require the presence of matter Energy Transfer Radiant Energy: energy that travels in the form of electromagnetic waves through empty space; includes visible light, ultraviolet rays, and infrared rays Radiation: the transfer of radiant energy by means of electromagnetic waves Hair straightener activity Read page 214 and 215 UV Rays What colour attracts the sun? 8.8 Managing the Transfer of Thermal Energy What are the three methods of energy transfer? Conduction – transfers thermal energy through walls Convection – currents produced by heaters warm the rooms Radiation – from the Sun; energy can be transferred to roofs through electromagnetic rays Our School What are some components of the school that work together to transfer energy throughout the school? Walls, roof, lights, air vents, floors, windows, doors, custodians, etc. What happens when a building is poorly designed? Some areas may be really hot and some may be very cold Expensive to heat because of poor insulation Read page 217 Thermal Energy Transfer What are ways we can reduce thermal energy transfer? Caulking gaps Replace old furnaces Closing blinds on sunny days Open windows at night to bring in cooler air Preventing Conduction Use insulating materials The higher the R-Value, the more difficult it is for energy to move through the material Insulation material (2.5 cm thick) wood fibreglass batt cellulose polystyrene foam board R-Value 0.71–1.41 3.2–3.6 3.1–3.7 3.6-5.0 Green Roofs 10% reduction in heat costs during the winter 25% saving in air conditioning costs in the summer Read page 218 - 220