3 Types of Heat Transfer
advertisement
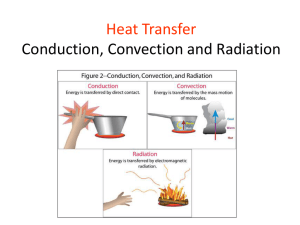
3 Types of Heat Transfer 6th Grade 1) Why are some of Earth’s layers solid and others liquid? 2) Why doesn’t the Earth melt? 3) Why do Earth’s layers change? The magic answer: HEAT TRANSFER! • What is a good definition for Heat Transfer? Heat Transfer: Remember this rule: Heat always moves from a warmer substance to a cooler substance • (ex. holding an ice cube will make your hand begin to feel cold in a few seconds.) • What are the 3 types of Heat Transfer? Heat Transfer: • 1) Radiation • 2) Conduction • 3) Convection What type of heat transfer is Radiation? 1) Radiation • The transfer of energy through space • Happens with no direct contact between a heat source and an object • What are examples of radiation? Examples of Radiation: • Sunlight is radiation that warms the Earth’s surface • When you feel heat from a fire without touching the flames What type of heat transfer is Conduction? 2) Conduction: • Heat transfer between materials that are touching • What are examples of Conduction? What are examples of Conduction? • Example: When you walk barefoot on hot concrete • Example: When a hot pot of water heats up a metal spoon. • Example: A cold cast iron skillet is placed onto a stovetop. When the stove is turned on, the skillet becomes very hot due to the conduction of heat from the burner to the skillet. What are examples of Conduction? • A cube of ice is placed into your hand. Over time, heat conducted from the your hand to the ice cube will cause the ice to melt. • When an athlete warms sore muscles with a heating pad What are examples of Conduction? • When a piece of hot lasagna is placed onto a porcelain plate, the plate will feel warm to the touch after several minutes due to the conduction of heat from the just-cooked food to the plate on which it sits. • A shirt is placed on an ironing board to be ironed. Heat from the iron is conducted to the shirt, making it easy to iron out all those unsightly wrinkles and make the shirt look sharp. What type of heat transfer is CONVECTION? 3) Convection • Movement of currents within a fluid • When a liquid or gas is heated, the particles expand, or become less dense and rise • When particles cool, they become more dense, and sink back to the bottom • This creates continuous convection cycles What are the three important things to remember that cause convection cycles to happen? Convection is caused by: • Heating and cooling of the fluid • Changes in the fluid’s density • The force of gravity During the convection cycle, as the warm particles expand and rise to the top, is the density of these particles increasing or decreasing? Density is decreasing because as the particles get warmer, they expand (take up more room) and therefore become less dense. As particles cool down, is the force of gravity stronger or weaker? As particles cool down, their density is increasing, so the force of gravity is stronger. Remember that objects that are more dense have a higher gravitational pull . Which cylinder has a higher density? Answer –the one on the right. It has more tightly packed particles. • Warmer particles become LESS dense because the same number of particles expand (are farther apart) and take up more space Where in the Earth’s interior does convection occur? Answer: THE MANTLE Remember our study of the Sun? The same thing is happening in the Earth’s mantle Earth’s Mantle • As the core heats the lower mantle (which is solid), it becomes less dense so rises through the Asthenosphere to the Lithosphere • The Lithosphere is cooling and becoming more dense, so it sinks into the Asthenosphere • This is a continuous process –Convection Cycle • These convection cycles happen over millions of years Examples of heat transfer by Convection: Examples of heat transfer by Convection: • Heating a pot of water over a flame • Cold air from an open freezer sinking to the floor