November Q2 - pg. 7 - MsPetersensScienceScholars
advertisement

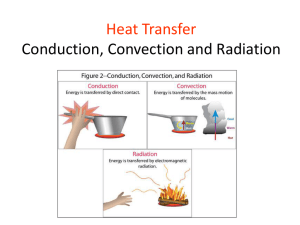
November 15 Q2 - pg. 13 • Daily Goal: We will be able to compare and contrast convection and conduction. • Homework: Gist Science Starter: 1. Explain how Kongming Lanterns work. 2. Do you think that all heat is transferred through air particles? Explain your answer. Conduction ***WRITE THIS DOWN*** • Conduction is the transfer of energy from one molecule to another. • This transfer occurs when molecules hit against each other • Conduction takes place in solids, liquids, and gases Let’s learn the sign for conduction! Conduction **WRITE THIS DOWN** Conduction is heat energy transferred through direct contact Examples: Pan on stove Conduction • The fast particles (the hot ones) will transfer some of their kinetic energy to the slow particles (the cold ones). This will make the slow particles move faster (and therefore have more heat). • This happens most often in solids, because in solids the particles are packed closely together. Examples of Convection • What are some examples conduction that you can you think of? • Make a list of examples in your notebook. Write down at least 4. • We will make a list of your ideas. Add to the list in your notebook if someone mentions an example that you don’t have. In your notebook, create a chart that looks like this: Conduction Convection In your notebook, categorize each of the following examples as either conduction or convection: • The heat you feel from a fireplace Frying a pancake A Warm Breeze Ice Melting in Your Hand Your hands being heated by hand warmers A radiator heating a room Touching a hot handle of a pan In your table groups, you will: • Create a poster-sized Venn diagram comparing and contrasting convection and conduction. • Each of you will have a team role. • Your poster must include: – At least 3 comparisons in each section (9 total) – At least 3 examples of convection and 3 examples of conduction – Illustrations of each example Radiation • Heat travels from the sun by a process called radiation. • Radiation is the transfer of heat by waves. • In addition to the sun, light bulbs, irons, and toasters radiate heat. • When we feel heat around these items, however, we are feeling convection heat (warmed air molecules) Radiation • Radiation is the transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves. • What is super fun about radiation is that it does NOT require any matter. (It can happen in empty space!) Examples of Radiation • The best (and most common) examples of radiation are from the sun and from heat lamps. • Draw one of those on your foldable. Make sure to label the direction of heat transfer (from hot to cold). Heat transfer • Can we have 3 methods of heat transfer at once? YES! Radiation Definition: Transfer of heat through space in the form of electromagnetic waves Example: Beachgoer gets sunburned Conduction,Convection, or Radiation? • The heat you feel from a fireplace • This type of heat transfer causes techtonic plates to move • boiling water • Heat you feel from a hot stove • Frying a pancake • fast particles colliding with slower particles • • • • • • • • • air travels this way transfer through solids transfer through space moves as a wave moves as a current sun rays reaching earth occurs with fluids a coil on an electric stove this type of transfer is affected by color