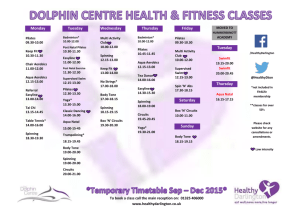
Pilates study guide
advertisement

Pilates History • It was created in the 1920s by the physical trainer Joseph Pilates (1880-1967) for the purpose of rehabilitation. Some of the first people treated by Pilates were soldiers returning from war and dancers such as Martha Graham and George Balanchine to strengthen their bodies and heal their aches and pains. Since the 1920s, the basic tenets that Joseph Pilates set down have been preserved, and to this day, even with some modifications, the Pilates remains true to its origins. • Pilates originally called his work Contrology. He considered this to be a body/mind/spirit approach to movement founded on the integrative effect of principles such as centering, concentration, control, precision, breath, and flow. Pilates and Principles.. • Two of the key elements of Pilates are core muscle strength and spinal alignment. The core musculature is loosely defined as the spine, abdomen, pelvis, hips, and the muscles that support these structures. Some of the main core muscles are the erector spinae (located in your back along your spine), the internal and external obliques (the sides of your abdomen), the transverse abdominis (located deep in your gut, this muscle pulls your belly button in toward your spine), the rectus abdominis (the "six-pack"), and hip flexors (in your pelvis and upper leg). Pilates is resistance, anaerobic exercise; however, the heart rate will certainly rise. • Pilates focuses on improving flexibility, strength, Contrology and principles Whether one is working out on a mat or using Pilates equipment, like the reformer or Cadillac, these basic principles infuse each exercise with intention and fullness of expression: 1. Centering: Physically bringing the focus to the center of the body also called he powerhouse (core) area between the lower ribs and pubic bone. 2. Concentration: bringing full attention and commitment to the exercise. 3. Control: Every Pilates exercise is done with complete muscular control. No body part is left to its own devices. . 4. Breath: using a very full breath in his exercises. Most Pilates exercises coordinate with the breath, and using the breath properly is an integral part of Pilates exercise. 5. Flow: Pilates exercise is done in a flowing manner. Fluidity, grace, and ease are goals applied to all exercises. The energy of an exercise connects all body parts and flows through the body in an even way. 6. Precision: In Pilates, awareness is sustained throughout each movement. There is an appropriate placement, alignment relative to other body parts, and trajectory for each part of the body The Basic 10 mat exercises… 1. Warm-up 2. The hundred 3. The roll-up 4. The roll-over 5. One leg circle 6. Rolling like a ball 7. Single leg stretch 8. Double leg stretch 9. Spine stretch 10. Open leg Rocker This is just an example of basic beginner moves. They can be modified depending on your level of fitness.