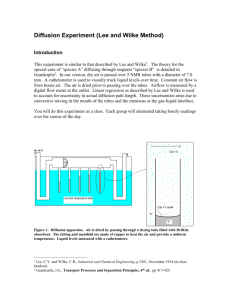
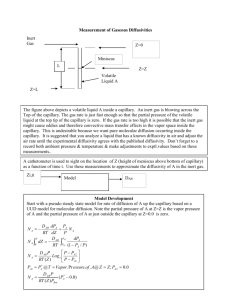
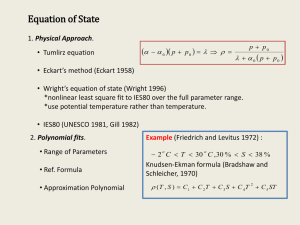
But……. tortuosity is hard to determine Predicting Effective Diffusivity
advertisement

Soil Gas-Phase Diffusion Dr. John Norman The Precision Agricultural Landscape Modeling System (PALMS) Monday, 1:00 – 2:00 pm., 3140 Agronomy Diffusion Definition Mathematical Model: Fick’s Laws Major Influences: temp., molecular weight, media it diffuses through Why Important and examples: • Rate dependent reactions • Gas Diffusion in Soil Will the diffusion flux differ in soil than bulk air? YES!...diffusivities will be different •Fractional volume for transport •Pores •Size and distribution •Air-filled porosity and tortuosity •Biological •Plant roots, earthworms Effective Diffusivity Fractional volume for transport Effective Diffusivity in Soil Pore Shape Effective Diffusivity in Soil Pore-Size Distribution Effective Diffusivity in Soil Air-filled porosity Effective Diffusivity in Soil Tortuosity Effective Diffusivity in Soil Tortuosity Predicting Effective Diffusivity Air-filled porosity and tortuosity •Buckingham: D(ε)/Da = к ε 2 •Water-induced linear reduction (WLR) Model D(ε)/Da = ε 1.5 (ε / ϕ) •Marshall: D(ε)/Da = ε 1.5 •Penman: D(ε)/Da = 0.66 ε Predicting Effective Diffusivity Air-filled porosity and tortuosity Moldrup: D(ε)/Da = k*(ε2.5)/ϕ But……. tortuosity is hard to determine Luo et al. SSSJ. 2008. No-till silt loam soil in Pennsylvania under corn, soybean, and alfalfa rotation Predicting Effective Diffusivity • Estimate • Assumptions in equations • Quick and Cheep Measuring Effective Diffusivity • Actual values • May need many measurements to represent site • Timely, Laborious, and Expensive Measuring Soil as Diffusivity Laboratory Analysis Measuring Soil as Diffusivity Laboratory Analysis Ln [(C – Cs)/(C0 – Cs)] • Soil core of known dimensions • Measure O2 vs. time • Calculate apparent gas diffusivity Dp = apparent diffusivity t = time (-Dp α2)/ε ε = air-filled porosity C = gas chamber O2 conc. Cs = ambient O2 conc. C0 = initial gas chamber O2 conc. αl = 0.895(hl)^(0.4599) l = core length time h=ε/a a = gas chamber volume per cross-sectional area Rolston, D.E. and P. Moldrup. 2002. Gas Diffusivity. Methods of Soil Analysis. SSSA. No. 5 Part 4. p. 1113 – 1139. Soil-gas exchange Which Dominates? Advection Diffusion Measuring Atmospheric Gas Exchange In-situ Analysis Measuring Atmospheric Gas Exchange HEADS UP!!!! When and Where? Dynamic system •Diurnal temperature cycle (soil breathing) •Atmospheric pressure changes and wind pumping •Soil water content and spatial variability of Ф •Biological activity (Source/Sink) •Roots (type, growth stage, distribution, etc.) •Microorganisms (type, food source, etc.) Class Over