10-Atmos2
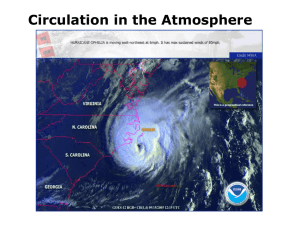
Circulation in the Atmosphere
Circulation in the atmosphere
How does planetary rotation affect fluid motions?
• Additional forces in the rotating frame of reference
– Centrifugal force Geoid
– Coriolis force
Coriolis force
Exmaple: playing catch on a merry-go-round
• Straight path in inertial (non-rotating) frame
• Deflection to the right in rotating frame
Coriolis force
• In northern hemisphere, planetary rotation is
counter-clockwise.
• A moving object is deflected to the right in rotating frame of reference
Coriolis force
• What is the sense of planetary rotation in the southern hemisphere?
- Looking down onto the south pole, planetary rotation is clockwise
• Which direction would Coriolis force defect a moving particle in the southern hemisphere?
- A moving object is deflected to the left in the southern hemisphere
Latitudinal variation of Coriolis force
• Projecting the merry-go-round on the planet
• Parallel rotation axis at the pole
Maximum Coriolis deflection
• Perpendicular rotation axis at the equator
No Coriolis deflection
General circulation (non-rotating atmosphere)
Hadley cell
• Rising air at tropics
• Sinking air at poles
• Poleward flow in the upper atmosphere
• Equatorward flow in the lower atmosphere
General circulation (rotating atmosphere)
Hadley cell confined in low latitudes
• Rising air at tropics
• Sinking air at subtropics
• Equatorward flow deflected westwards
(trade wind)
• Poleward flow deflected eastwards
(westerly wind)
Tank demo
Hadley circulation: very low rotation rate
(~ 1-2 RPM)
Low lat.
“Pole” Low lat.
Tank demo: Hadley cell
Upper-level westerly wind
Low-level trade wind
Hadley cell dominates low-latitude circulation
What controls the middle-high latitude circulation?
Mid-latitude cyclones
• Weather system
– Strong rotation effect generates turbulent motions
– High and low pressures
– Fronts: separating warm tropical air and cold polar airs
Synoptic scale circulation
High pressure
Dry air sinking
Sunny weather
Air spirals out
Clockwise
Low pressure
Moist air rising
Rainy weather
Air spirals in
Counter-clockwise
Tank demo
Mid-latitude cyclones: high rotation rate
(~ 5+ RPM)
Low lat.
“Pole” Low lat.
Tank demo
Mid-latitude cyclones: high rotation rate
(~ 5+ RPM)
Putting it altogether
“Eddy” regime
Variable weather
Westerly wind
Subtropical high
“Hadley” regime
Intertropical convergence zone
(ITCZ)