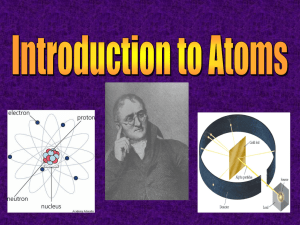
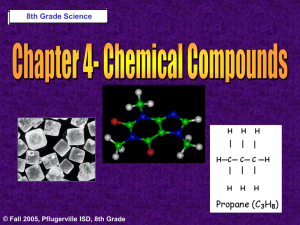
Heat POWERPOINT - Bowling Green Independent Schools
advertisement

What is Temperature? What Do You Think? What happens when you use a thermometer to measure temperature? © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade Temperature Depends on Kinetic Energy •Kinetic Energy is the energy of motion •The faster the particles of matter move, the more kinetic energy they have © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade What is Temperature? Measuring Temperature •Temperature is a measure of the Average Kinetic Energy of a substance •When you measure temperature, you are measuring the average motion of the atoms © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade What is the difference between temperature and heat? Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of atoms. Thermometers are used to measure temperature This means: the higher the temperature, the faster the atoms move the lower the temperature, the slower the atoms move Less Heat © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade More Heat What is Temperature? Temperature is expressed by one of 3 scales: © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade What is Temperature? Thermal Expansion- As temperature rises, volume (size) increases © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade What is Temperature? Thermal Expansion •When the metal rails in this picture heated up, they increased in length and volume •Thermal Expansion caused the rails to buckle and bend © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade What is Temperature? Thermal Expansion •The asphalt in the road expands when heated and contracts when cooled •This results in cracks and potholes due to Thermal Expansion © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade THERMAL EXPANSION The spreading of particles (atoms) or increased volume (size) when an object is heated is known as THERMAL EXPANSION © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade THERMAL EXPANSION. If energy is added to atoms, they move faster. The faster they move, the further apart they move. This spreading out of atoms happens in solids, liquids and gases. Thermal expansion is why running a tight jar lid under warm water loosens the lid. *pg 154 © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade What is Heat? What Do You Think? Which is warmer, the tile or the rug on a bathroom floor? © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade What is Heat? Heat- A Transfer of Energy •Heat is the transfer of energy between objects or particles that are at different temperatures © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade Another word for heat is THERMAL ENERGY. Hot objects contain more thermal energy than cold objects . © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade What is Heat? Heat- A Transfer of Energy •Energy moves from the warmer object to the cooler object until both are the same temperature •This is known as Thermal Equilibrium © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM The point at which two objects reach the same temperature. © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade What is Heat? Reaching Thermal Equilibrium © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM No energy transfer occurs © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade What is Heat? Energy is Transferred by 3 Methods: © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade What is Heat? •Conduction is the transfer of thermal energy through direct contact •Hold a metal wire in a flame and energy travels from atom to atom until it burns your hand © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade CONDUCTION Transfer of heat from one substance to another by direct contact. Happens within and between objects that touch each other Examples: Sauce pan on a stove top, metal spoon in a bowl of soup, ice melting in a warm hand, hot shower, walking on hot coals © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade Objects that heat up easily are called CONDUCTORS. Metals are the best conductors Metal objects feel cold because they conduct heat AWAY from your hand © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade Objects that DO NOT heat up easily are called INSULATORS. Things like glass,wood, plastic and rubber are good insulators Which parts of the pan are conductors and which are insulators? © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade What is Heat? Convection •Convection is the transfer of thermal energy by the movement of a liquid or a gas •Convection is seen as hot material rises and cool material sinks © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade CONVECTION Transfer of heat in liquids and gases ONLY Heat moves up and down in a circular motion called a CONVECTION CURRENT Heated liquids and gases are less dense & rise carrying heat with them Examples: hang gliders, soaring birds, home furnace heating & circulating air © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade Convection currents cause the Earth’s tectonic plates to move about. © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade What is Heat? Radiation © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade •Radiation is the transfer of energy through matter or space through light energy, such as visible light and infrared waves •Radiation is the only type of energy transfer where the objects don’t have to touch RADIATION transfer of heat through empty space in form of infrared radiation waves (what we think of as heat waves) Examples: blacktop heats up on a sunny day, hot sand on a beach, electric heaters. © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade Explain how each of these uses radiant heat. © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade Harcourt Science: States of Matter BBC: Science BrainPop: States of Matter © Fall 2005, Pflugerville ISD, 8th Grade Unit A : Chapter 1 : Section 1