Class Slides
advertisement

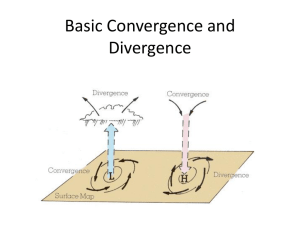
ATMO 336 Weather, Climate Society Cyclones, Cyclogenesis Weather Forecasting Recall: Uniform Circular Motion Requires Acceleration/Force Circle Center Circular Path Initial Velocity Final Velocity Final Velocity Initial Velocity Acceleration directed toward center of circle Centripetal (center seeking) acceleration is required for curved flow, i.e. to change the direction of the velocity vector! Flow Around Curved Contours Assume PGF constant size along entire channel L H Centripetal Acceleration is Required for Air Parcel to Curve Forces for Curved Flow Assume PGF constant size along entire channel PGF Wind PGF PGF CF CF Wind Centripetal = PGF + CF CF Centripetal << PGF or CF Gradient Wind Balance Gradient Wind Balance: End Result Assume PGF constant size along entire channel Slower than Geo Wind Faster than Geo Wind Wind speeds are Slowest at trough Fastest at ridge Therefore, wind speeds Increase downwind of trough Decrease downwind of ridge Gradient Wind Balance Assume PGF constant size along entire channel 2 1 Speeds and Areas: Increase downwind of trough Decrease downwind of ridge Divergence and Convergence Assume PGF constant size along entire channel Divergence: Horizontal Area Increases with Time Convergence: Horizontal Area Decreases with Time Parcel Shapes: Stretch Downwind of Trough so Area Increases Compress Downwind of Ridge so Area Decreases Divergence and Convergence Assume PGF constant size along entire channel Large Small Mass transport across channel Vertical Motion Ridge Trough Ridge Gedzelman, p249 Mass Conservation leads to Upward motion beneath regions of divergence Downward motion beneath regions of convergence Super-geostrophic Sub-geostrophic Divergence Convergence Where Winds are Divergent? Regions downwind of 500 mb troughs are favorable for surface cyclones and upward motion. faster winds Ridge Trough slower winds Cyclogenesis can only occur where mass is being removed from the column overhead. Mass loss produces surface pressure falls. What Increases Divergence? faster winds Ridge Trough slower winds 1) Stronger PGF because faster winds require larger centripetal accelerations. Divergence stronger along axis of jet stream. What Increases Divergence? faster winds Ridge Trough slower winds 2) Bigger amplitude waves because the sharper curvature requires larger centripetal accelerations. Divergence stronger downwind of larger amplitude troughs. What Increases Divergence? faster winds Ridge Trough slower winds 3) Shorter wavelength because the sharper curvature requires larger centripetal accelerations. Divergence stronger downwind of shortwave troughs. tilt Vertical Structure tilt Fundamental Fact: Cyclone deepens only if divergence in column exceeds convergence! This condition can occur if the system tilts toward the west with height Westward tilt aligns upper-level (UL) divergence over the surface low and … Results in low deepening Ahrens, Meteorology Today, 5th Ed. Friction Induced Vertical Motion downward motion upward motion Ahrens, Fig 6.21 Divergence Convergence Divergence Surface Convergence and Divergence Summary: Curved Flow & Friction • Curved Flow Requires Centripetal Acceleration Difference between PGF and Coriolis Force Speed Changes => Convergence-Divergence • Frictional Force Causes Winds to Turn toward Low Pressure Important in the lowest 1 km above the Surface Leads to Convergence-Divergence • Curvature and Friction Produce Cyclones and Vertical Motions Simplistic Model for Homework H Cold L Surface Anticyclone L H Warm Surface Cyclone H Surface Anticyclone ATMO 336 Weather Forecasting Reasons to Forecast Weather • Should I bring my umbrella to work today? • Should Miami be evacuated for a hurricane? • How much heating oil should a refinery process for the upcoming winter? • Will the average temperature change if CO2 levels double during the next 100 years? • How much to charge for flood insurance? These questions require weather-climate forecasts for today, a few days, months, years, decades Forecasting Questions • • • How are weather forecasts made today? How accurate are current weather forecasts? How accurate can weather forecasts be? Types of Forecasts Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) - use mathematical models of physics principles to forecast future state from current conditions. Process involves three major phases 1. Analysis Phase (most expensive piece) 2. Prediction Phase (modeling, computing) 3. Post-Processing Phase (use of products) To justify NWP cost, it must beat no-brainer forecasts of persistence and climatology Analysis Phase • Current weather conditions are observed around the global (surface data, radar, weather balloons, satellites, aircraft). • Millions of observations are transmitted via the Global Telecommunication System (GTS) to the various weather centers. • U.S. center is in D.C. and is named National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) Analysis Phase • The operational weather centers sort, archive, and quality control the observations. • Computers then analyze the data and draw maps to help us interpret weather patterns. Procedure is called Objective Analysis. Final chart is referred to as an Analysis. • Computer models at weather centers make global or national weather forecast maps Surface Data Sparse data over oceans and Southern Hemisphere Courtesy ECMWF Surface Buoy Reports Some buoy data over Southern Hemisphere Courtesy ECMWF Radiosonde Coverage Little data over oceans and Southern Hemisphere Courtesy ECMWF Aircraft Reports Little data over oceans and Southern Hemisphere Courtesy ECMWF Weather Satellites Geostationary Polar Orbit Ahrens, Figs. 9.5 & 9.6 Satellite observations fill data void regions Geostationary Satellites High temporal sampling Low spatial resolution Polar Orbiting Satellites Low temporal sampling High spatial resolution sweet spot T from (Mostly) GEO Satellites Courtesy ECMWF T from Polar Satellites Courtesy ECMWF Atmospheric Models • Weather models are based on mathematical equations that retain the most important aspects of atmospheric behavior - Newton's 2nd Law (density, press, wind) - Conservation of mass (density, wind) - Conservation of energy (temp, wind) - Equation of state (density, press, temp) • Governing equations relate time changes of fields to spatial distributions of the fields warmer to south + southerly winds warming Atmospheric Models Must contain representations of many of complex physical processes to produce a good forecast Prediction Phase • Analysis of the current atmospheric state (wind, temp, press, moisture) are fed into the model equations • Equations are solved for a short time period (~5 minutes) over a large number (108) of discrete locations called grid points • Grid spacing is 5 km to 50 km horizontally and 100 m to 500 m vertically Model Grid Boxes Forecast average conditions within grid boxes shaped like brownies “A Lot Happens Inside a Grid Box” (Tom Hamill, CDC/NOAA) Rocky Mountains Approximate Size of One Grid Box for NCEP Global Ensemble Model Note Variability in Elevation, Ground Cover, Land Use 50 km Denver Source: www.aaccessmaps.co 13 km Model Terrain Big mountain ranges, like the Sierra Nevada, are resolved. But isolated peaks, like the Catalina’s, are not evident. 100 m contour Take Home Points Forecasts are needed by many users There are several types of forecasts Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) Use computer models to forecast weather -Analysis Phase -Prediction Phase -Post-Processing Phase Humans modify computer forecasts