Factors of Climate
advertisement

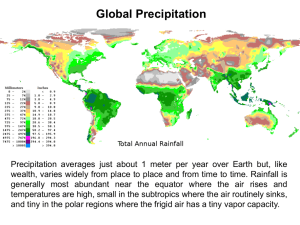
Chapter 25.1 “Factors that Affect Climate” Modified from many sources & Holt CA Earth Science by L. Smith Factors That Affect Climate CLIMATE = The AVERAGE weather conditions over a LONG period of time CLIMATE = WEATHER Factors That Affect Climate CLIMATE = most often described by: AVERAGE TEMPERATURE and ANNUAL PRECIPITATION Factors That Affect Climate I. Latitude II. Heat Absorption & Release III. Topography Factors That Affect Climate I. Latitude • The sun’s rays strike the equatorial region at a much more direct angle than the poles, making the average temperature at the poles much colder and the average temperature at the equator much warmer. Latitude http://www.geogrify.net/GEO1/Lectures/EnergyAtmosphere/SolarEnergy.html • Solar energy striking the Earth’s surface near the poles is less intense than radiation striking the Earth near the equator. Latitude Latitude Global Wind Patterns Differing amounts of solar energy, and the spinning of the Earth, create different wind patterns at different latitudes . Latitude Global Wind Patterns Wind patterns at different latitudes then influence precipitation patterns. Factors That Affect Climate II. Heat Absorption & Release • Different surfaces heat and cool at different rates creating wind patterns and ocean currents. Heat Absorption & Release Land vs. Water The differential heating and cooling of land and water creates winds. Land heats AND cools faster than water. Heat Absorption & Release Specific Heat & Evaporation Specific heat is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of a substance 1 degree C. Heat Absorption & Release Specific Heat & Evaporation Water requires a larger amount of energy to increase temperature than most substances. Evaporation of water absorbs a lot of energy too (think sweat!). Heat Absorption & Release Ocean Currents Ocean currents can have a large influence on air masses over the land they contact. http://geology.uprm.edu/Morelock/2_image/ocncur.jpg Heat Absorption & Release El Niño Southern Oscillation • El Niño - the name given to the periodic warming of the ocean that occurs in the central and eastern Pacific. • At irregular intervals of 3-7 years, these warm countercurrents become unusually strong and replace normally cold offshore waters with warm equatorial waters. Heat Absorption & Release El Niño Southern Oscillation • A major El Niño episode can cause extreme weather in many parts of the world. Increase precipitation and landslide activity in southern California and the Southwest Drought to the northern Rocky Mountains Heat Absorption & Release Normal Conditions Heat Absorption & Release Normal Conditions Normally, strong trade winds blow from the east along the equator, pushing warm water into the Pacific Ocean. Heat Absorption & Release El Niño Conditions Heat Absorption & Release El Niño Conditions An El Niño condition results from weakened trade winds in the western Pacific Ocean near Indonesia, allowing piled-up warm water to flow toward South America. Heat Absorption & Release La Niña • Researchers have come to recognize that when surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific are colder than average, a La Niña event is triggered that has a distinctive set of weather patterns. Droughts in parts of the South and Southwest from Arizona to Arkansas and Louisiana Above normal precipitation in the Northwest and the Tennessee Valley area Heat Absorption & Release Seasonal Winds Monsoons are the seasonal reversal of wind direction associated with large continents, especially Asia (which affects the Indian subcontinent). http://www.mrdowling.com/images/612monsoons.png Heat Absorption & Release Monsoons • In summer, the wind blows from sea to land.(wet) • In winter, the wind blows from land to sea.(dry) http://volney-bodley-weather- Monsoon Photos More about monsoons--click here Factors That Affect Climate III. Topography • Topographic features such as mountains play an important role in the amount of precipitation that falls over an area. Elevation Topography Elevation is height above sea level Temperature generally decreases as elevation increases. The Rain Shadow Effect As humid air on the windward side of the mountain moves up the slopes it cools, condenses, and forms clouds and rain. By the time the air reaches the leeward side of the mountain, most of the moisture is lost. The Rain Shadow Effect RAIN SHADOW http://classconnection.s3.amazonaws.com/436/flashcards/774436/jpg/picture11320597452956.jpg The dry area on the leeward side of the mountain is called a rain shadow. The Rain Shadow Effect http://www.geography.hunter.cuny.edu/~tbw/wc.notes/15.climates.veg/climate/B ... The Rain Shadow Effect The dry area on the leeward side of the mountain is called a rain shadow. http://www.sierranevadaphotos.com/geography/sierra_precipitation.asp Climate Data for Two Cities This climate graph shows data for two cities, both located in Arizona. Phoenix has an elevation of 338 m and Flagstaff has an elevation of 2134 m. • How does the elevation affect the annual temperature and precipitation? • What causes this difference to occur? Other Factors That Affect Climate IV. Bodies of Water • Large bodies of water, such as lakes and oceans, alter the climate of an area. • Places downwind of a large body of water generally have cooler summers and milder winters than places of the same latitude that are further inland. Other Factors That Affect Climate IV. Bodies of Water • Coastal areas (or areas near large lakes like the Great Lakes) generally have more precipitation than inland areas. http://quizlet.com/15961300/print/ Other Factors That Affect Climate V. Atmospheric Circulation • Global winds are another factor that influences climate because they distribute heat and moisture around Earth. Other Factors That Affect Climate V. Atmospheric Circulation • Low-pressure zones at the equator and in the sub-polar regions form clouds that drop much more annual precipitation in the form or rain or snow depending on the average temperatures of the area. http://www.weatherwizkids.com/globalcirculation.gif Other Factors That Affect Climate V. Atmospheric Circulation Notice the cloud cover over the equator (equatorial low) and clear skies over the tropics (subtropical highs.) Other Factors That Affect Climate VI. Vegetation • Vegetation can affect both temperature and precipitation patterns in an area by influencing how much of the Sun’s energy is absorbed and how quickly this energy is released. Other Factors That Affect Climate VI. Vegetation • Plants release water vapor through their leaves into the air via transpiration. • Vegetation also releases particles that act as cloud seeds and increase precipitation. http://vjh.flbsd.mb.ca/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/transpiration.jpeg