Photosynthesis
advertisement
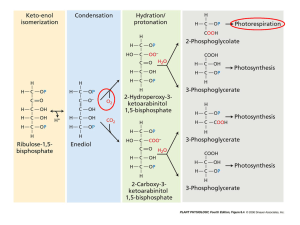
Energy acquisition and biochemical pathways: Photosynthetic pathways (C3, C4, CAM) Questions • Lectures now posted on wiki • Discussions: – Mariana: posting paper and questions for this week – Dilys: will be picking a paper to post for next week • Any questions? Ferns Gymnosperms Angiosperms Carbon dioxide uptake by plants • CO2 is – About 0.038% in atmosphere – What about inside leaves? – But remember CO2 uptake is in exchange for H2O loss. What about differences in water across the leaf surface? What is photosynthesis? RUBISCO • RUBISCO, drives – Carbon fixation in photosynthesis and releases oxygen (but has a low affinity for CO2), – Carbon release in photorespiration with oxygen as substrate. Photosynthesis RuBP + CO2 2PGA Photorespiration RuBP + O2 glycolate •Photorespiration: No carbon fixed but glycolate can be used in amino acid synthesis Photosynthetic strategies • Most plants (C3): fix carbon dioxide initially as phosphoglycerate (PGA), a three-carbon compound. – Enzyme is ribulose bi-phosphate carboxylaseoxidase (RUBISCO) – Biochemical cycle is called Calvin cycle. But, if it is really hot and dry water uptake is a problem. What to do? Hatch and Slack cycle • Some plants, mainly tropical grasses, C4: first combine carbon dioxide with phosphoenol-pyruvate (PEP), into a four carbon compound – oxaloacetate. Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM) • Third photosynthetic strategy (CAM): first found in plants in the family Crassulaceae and was therefore called Crassulacean Acid Metabolism. • Plants in other families also use this mode of carbon fixation (lots of succulents and epiphytes). What do you think the main advantages and disadvantages of each strategy is? Evolution of C4 in grasses Question • Why did C4 evolve in grasses? – Dogma: A response to rising temperatures and lowering CO2 – To test this, for 1230 grass spp, 1.1 million specimens • GBIF: georeference points • Climate: CRU (Climate Resource Unit) • DNA sequences: With PHLAWD, built a phylogeny – Chloroplast regions: atpB (59 taxa), matK (266 taxa), ndhF (437 taxa), rbcL (251 taxa), rpl16 (176 taxa), and trnL-trnF (810 taxa) – Nuclear regions: phyB (93 taxa) and the internal transcribed spacer (ITS; 753 taxa) Ferns Gymnosperms Angiosperms Poales Poaceae Shady Question • Why did C4 evolve in grasses? – Forget dogma: • Grasses were historically warm adapted • C4 evolution was in response to a drop in precipitation • So, the shift was probably from tropical rainforests understories to open tropical savannahs and grasslands!!! • The question then becomes, when, why, and how did C3 grasses evolve cold tolerance?