Building structure & Earthquake resistant capacity
advertisement

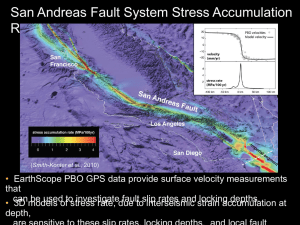
Building structure & Earthquake resistant capacity YAN WENLI A9SJ2002 2010/05/07 Outline Building structure types Adobe Masonry Reinforced Concrete Steel Timber Earthquake resistant capacity showed in earthquake cases 1995/01/17 Hyogo-ken earthquake, Japan 1999/08/17 Kocaeli earthquake, Turkey 2003/12/26 Bam earthquake, Iran 2008/05/12 Wenchuan earthquake, China Building structure I Adobe Raw material Sand Clay Manure Water Fibrous or organic material (sticks and/or straw) Shaped into bricks using frames and dried in the sun Building structure I Advantage: Durable(account for some of the oldest extant buildings on the planet) Great thermal mass(for living comfort) Disadvantage: Susceptible to seismic damage Great weight of adobe bricks Building structure II Masonry Raw material Brick Stone(marble, granite, travertine, limestone) Concrete Block Glass block tile Building structure II Advantage: Great thermal mass Heat resistance Resistance to projectiles Disadvantage: degradation of wall surfaces due to extreme weather Heavy and easy to crack Building structure III Steel Constituent • Iron(mostly) • Carbon(between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight) • Other alloying elements(such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten) Varying the amount of alloying elements and form of their presence in the steel controls qualities such as the hardness, ductility, and tensile strength of the resulting steel. Building structure III Advantage: High strength Light weight Great ductility and toughness Disadvantage: Expensive Vulnerable to fire Building structure IV Reinforced Concrete concrete in which reinforcement bars ("rebars"), reinforcement grids, plates or fibers have been incorporated to strengthen the concrete in tension. Building structure IV Advantage: Enlarged tensile strength Durable Resistance of fire Disadvantage: Expensive Technical difficulty Building structure V Timber Timber framings refer to structures utilizing heavy timbers jointed via pegged mortise and tenon joints. Building structure V Advantage: allowing great rapidity in erection on site and more precise alignments. (an "average"-sized timberframe home can be erected within 2–3 days) Light weight Great Elastic property Disadvantage: Poor prevention of capillary movement of water Burn easily Earthquake archive I 1995/01/17 Hyogo-ken earthquake, Japan RC structure – not collapse easily Earthquake archive I Fire-vulnerable timber structure should be paid great attention, as fire usually take place together with and earthquake. Earthquake archive II 1999/08/17 Kocaeli earthquake, Turkey Earthquake archive III 2003/12/26 Bam earthquake, Iran Masonry structure Earthquake archive IV 2008/05/12 Wenchuan earthquake, China Expose “tofu-dregs projects” (jerry-built projects, lowquality construction, Chinese: 豆腐渣工程) Building structure of reinforced concrete should have good earthquake resistant capacity. However, in the case that the steel bar is not thick enough, expected strength can not be supported. Conclusion In respect of earthquake resistant capacity, building structures of steel and timber are the best. However, reinforced concrete is an eclectic choice when taking into consideration the economic factor. To be mentioned, it’s important to produce and exploit high-quality RC rather than tofu-dreg material.