Ancient World History - Ash Grove R

Ancient World History
Chapter 3
Early Civilizations in India and
China
Section 1
►
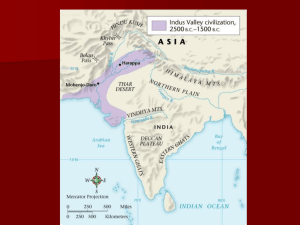
Cities of Indus Valley
Geography of the Indian
Subcontinent
►
Located in the region of South Asia or also known as the subcontinent of India
Large landmass that jets out from a continent
►
Today the second most populous region
►
Mountains to the North
Including the Himalayas
Geography of the Indian
Subcontinent (Con’t)
►
Regions
Three major zones
►
Northern Plains
► just south of the mountains
Ganges and Indus Rivers
►
Named India after the Indus River
►
Deccan Plateaus
Very arid and sparsely populated
►
Coastal Plains
Heavy monsoon rains
Major fishing and trading region
Geography of the Indian
Subcontinent (Con’t)
►
Monsoons
October, dry hot winds hit India
May-June
►
West summer monsoons
►
Delicate balance of rain desired
►
Cultural diversity
A Big number of languages, customs and traditions
Indus Valley Civilization
►
►
►
►
Original civilization appeared in about 2500 B.C. near Pakistan on the Indus River
Mysteriously vanished
Well Planned Cities
Two main cities
►
Harappa and Mohenjor Daro
3 mile circumference city with huge warehouses
Laid out in a grid pattern
Semi-modern plumbing
Merchants had a uniform system of measure and weights
Assumed well organized government and leaders
Indus Valley Civilization (Con’t)
►
People also known as Dravidians
►
Farming and Trade
Most people were farmers
►
First to cultivate cotton and weave it into cloth
Some people were merchants and traders
►
Sailed all the way to Sumer
►
Religious Beliefs
Polytheistic
►
Mother Goddess source of creation
Decline and Disappearance
►
Cities began losing quality of life
►
Possibly over ran by the Aryans with their horse drawn chariots
Aryans are from Ganges River region
Section 2
►
Kingdom of the Ganges
Aryan Civilization
►
►
Warriors from the Ganges River region
Most history comes from Vedes
►
Collection of prayers
Mostly nomadic herders who greatly valued cattle
Aryan Society
Three Groups work
►
Brahmins: Priest
►
Kshatriyas: Warriors
►
Vaisyas: Herders, merchants, farmers, artisans
►
Sudras: Farm workers, Laborers
Gave rise to a caste system
►
Social groups people are born into and cannot change
Aryan Civilization (Con’t)
►
Aryan Religious Beliefs
Polytheistic
Fierce Indra
►
Main Deity, God of War
►
Weapon was a Thunderbolt
Also honored monkey and snake Gods
However began moving to a single spiritual power, Braham
►
Spiritual power that resided in all things
►
Led to Mystics
People who devote lives to seeking spiritual truth
Expansion and Change
►
Aryans were led by Rajahs
Skilled war leaders, elected by assembly of warriors
►
From nomads to farmers
Learned farming from those they conquered
By 800 B.C. learned to make tools out of iron
By 500 B.C. Indian Civilization emerged
►
Blended by Aryans and Dravidians
►
New written language of sanskrit
2
Aryan Civilization
The Aryans destroyed and looted the civilization of the Indus Valley and built a new Indian civilization, which reflected the following characteristics:
Nomadic warriors
Built no cities and left no statues
Felt superior to the people they conquered
Religious teachings from the
Vedas
Polytheistic
People born into castes , or social groups, which they could not change
Epic Civilization
►
Mahabharata
India’s greatest epic
Contains Bhagavad-Gita
►
Shows Indian religious belief and becomes foundation of Hindu religion
►
Ramayana
Epic hero Rama saves his beautiful bride Sita
►
Rama and Sita become the model for men and women in Indian Culture
Looking Ahead
►
Aryan’s help bring about the religions of
Hinduism and Buddhism
Section 3
►
Early Civilization in China
The Geography of China
►
Most isolated of all early civilizations
►
Geographic barriers
West and southwest of China lies Mountains
►
Tien Shan and Himalayan Mountains
North of China lies Desert
►
Gobi Desert
Southeast of China lies thick jungles
East of China
►
Pacific Ocean
China Traded, even to the Middle East
The Geography of China (Con’t)
►
Main Regions
Rivers
►
Huang He (Yellow) River and Yangzi River
Regions
►
Xinjiang, Mongolia, Manchuria and Tibet (Xizang)
Most nomadic people in these regions
The River of Sorrows
►
Civilization started near Huang He
►
Needed to control river
Yellow from loess
►
Wind blown yellow soil
►
Flooding Devastated the region
China Under the Shang
►
1650 B.C. to 1027 B.C. Northern corner of China ruled by the Shang Dynasty
►
Government
Kings ruled small areas with Nobles governing most lands as clans
►
Groups of families
Social Classes
►
Mirrored other early civilizations
Peasant Life
►
Most people were peasants living in farming villages
Everyone farmed, built dikes, and fought alongside their Lords
Religious Beliefs
►
Polytheistic
Chief Goddess Shang Di
►
Brought Plants and Animals to earth
Did not pray to the God, but instead to great ancestors
►
Delicate balance between Yin and Yang
Yin
►
Earth, darkness and female forces
Yang
►
Heaven, light, and male forces
System of Writing
►
Used both pictographs and ideographs
►
Consulting the Ancestors for Wisdom
Oracle Bones
►
Wrote questions on a bone
►
Heated it up till the bone cracked
►
Interpreted the cracks
System of Writing (Con’t)
►
A difficult study
Chinese people must memorize up to 10,000characters
►
Each means a letter, word or idea
Used calligraphy
►
Fine handwriting
A force for unity
►
Spoken language was different throughout the regions of China, but the written language stayed the same
The Zhou Dynasty
►
Zhou from Western China overthrew Shang
Dynasty
►
Promoted Mandate of Heaven
Divine right to rule
Became a Dynastic Cycle
►
Dynasty in power till weak or corrupt
►
Then taken over by another Dynasty
►
Floods and Catastrophes signaled end of Dynasty
Chinese civilization took shape under the
Shang and Zhou.
Shang Dynasty
(1650 B.C.
–1027 B.C.)
Zhou Dynasty
(1027 B.C.
–256 B.C.)
Gained control of corner of northern China along Huang
He.
Drove off nomads from northern steppes and deserts.
Held complex religious beliefs.
Developed written language used by all Chinese people.
Overthrew the Shang.
Promoted idea of Mandate of
Heaven.
Set up feudal state.
Economy and commerce grew.
Population increased.
3
The Dynastic Cycle in
China
The dynastic cycle refers to the rise and fall of dynasties.
The Zhou Dynasty (Con’t)
►
A Feudal State
Federalism during the Zhou Dynasty
►
System of government in which Lords governed their lands but owed support to their ruler
►
Economic Growth
Ironworking developed
Better irrigation, roads, and canals
Use of coins, or money economy
►
Population explosion
Chinese Achievements
►
Made an accurate 365 ¼ days calendar
►
Silk making
Became biggest export
►
Later developed trade route to Middle East called
Silk Road
►
First Books
Made first books of thin wood or bamboo