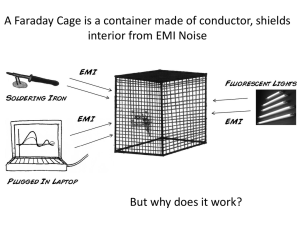
Transmission Line Mechanical Design: Conductors & Supports
advertisement

Mechanical Design of Transmission Lines General Considerations Electrical Considerations for T.L. Design: • Low voltage drop • Minimum power loss for high efficiency of power transmission. • The line should have sufficient current carrying capacity so that the power can be transmitted without excessive voltage drop or overheating. • Conductivity of Conductor: R = ρ.L/A , or R = L/Ϭ. A Where: L: Conductor length. A: Conductor cross sectional area. ρ: resistivity Ϭ: Conductivity (Ϭ= 1/ρ) • The conductor conductivity must be very high to reduce Conductor resistance R and hence reduce losses PL= 3 I2 .R Mechanical Considerations for T.L. Design: • The conductors and line supports should have sufficient mechanical strength: - to withstand conductor weight, Conductor Tension and weather conditions (wind, ice). - The Spans between the towers can be long. - Sag will be small. - Reducing the number and height of towers and the number of insulators. • Heat expansion coefficient must be very small. Rt = R0. (1 + α0 .t) αt = α0/(1+ α0.t) α t is the heat expansion coefficient at t. TYPES OF CONDUCTORS MATERIALS 1- All Aluminum Conductors (AAC) lowest cost – low mechanical strength Used for small span 2- Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced (ACSR) 1- Steel strands 2- Aluminum strands ACSR (26/7) Advantages of ACSR • High mechanical strength can be utilized by using spans of larger lengths. • A reduction in the number of supports also include reduction in insulators and the risk of lines outage due to flash over or faults is reduced. • losses are reduced due to larger diameter of conductor. • High current carrying capacity. 3- All Aluminum Alloy Conductor )(AAAC وهى عبارة عن سبيكة من األلمونيوم والماغنسيوم والسيليكون المعالجة حراريا له متانة عالية (أكبر نسبة متانة مع الوزن( – وبالتالى يمكنزيادة المسافة بين االبراج مما يقلل من التكلفة له مقاومة أقل وبالتالى يقلل من الفقد فى القدرة -غير معرض تآكل الجلفنة كما فى النوع السابق 4-Aluminum Conductor Alloy )Reinforced (ACAR وفيه استبدل القلب المكون من أسالك الصلب بقلب من أسالك من سبيكة من االلمونيوم Types of Supports • Wooden Poles • Reinforced Concrete Poles • Steel Poles • Lattice Structure Steel Towers Wooden Poles Reinforced Concrete Poles Steel Poles Lattice Structure Steel Towers األكثر استخداما فى الجهد العالى: األعلى نسبة متانة /الوزن األطول عمرا سهولة التركيب والتجميع تتحمل قوى ميكانيكية عالية يعيبها: وجوب دهانها من وقت آلخر تحتاج اساسات خرسانية– تكاليف نقلها عالية Types of Towers 1- Suspension Tower 2- Tension Tower 3- Angle Tower 4- End Tower 1- Suspension Tower 2- Tension Tower 3- Angle Tower 4- End Tower This type of towers exists in the beginning and at the end of the line which exposed to tension in one side. SAG AND TENSION CALCULATIONS Sag of Transmission Lines Sag of T.L depends on: - Conductor weight. Span length, Tension in the conductor, T Weather conditions (wind , ice). Temperature. Minimum Clearance between the ground and the conductor kV 0.4 11 33 66 132 220 400 C (m) 5.5 5.5 6.0 6.2 6.2 7.0 8.4 Conductor Spacing Spacing = (S )0.5 + V/150 Where: S: Sag in meters. V: Line voltage in kV.