ibdp_subjects_businessmgmt_swotamd
advertisement

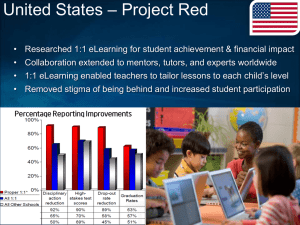
Company reviewed – Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) Introduction • AMD was founded in 1969 as a logic chip producing company. Since that day, they have developed into a large multi-national company that produces micro-processors (CPUs), mainly for computers. Currently in the market, there are only two major competitors, that is Intel and AMD. 1. Cheaper and more competitive products 2. Acquisition of ATI • Shared knowledge and technology base. • Able to simultaneously release Graphic cards and CPUs 3. Innovative ideas • The AMD Phenom™ Quad Core Processor technology, scheduled for release in 2008-2009 4. Popular among enthusiasts • Dunno leh 5. Growing market share • AMD saw its share of the x86 server processor market grow 51% in the quarter, from 7.4% to 11.2%, according to analyst firm Mercury Research. • July 2005, Information Week • Although Intel remains dominate in the market with 88.8% share, "you have to keep in mind that five years ago Intel's number was 100%," McCarron says. "I'm sure that AMD's success is not lost on Intel." Market share in CPUs 1. Weaker brand name • Most people associate PCs with Intel 2. Less popular in mainstream market • also dunno leh 3. Stiff competition • Since there are only two competitors in the industry, Intel and AMD, competition is heavy between the two. vs 4. Lesser market share Intel still dominates most of the market 5. Smaller production capabilities • AMD produces their own processors in Fabrication Plants, called "FABs". • To date, Intel owns many more FABs than AMD. • AMD has even considered giving up being in the fabrication business, due to losses. Image of AMD's future 300mm fab in Dresden Only real men have fabs. —Former AMD CEO, Jerry Sanders 6. Slower product availability • AMD products are generally released later than Intel’s • Resulting in lower sale figures, although lately AMD has been gaining higher sale records 7. Smaller profit margin • To remain competitive, AMD is forced to slash prices on it’s best selling models, like the Athlon 64 FX Series. • Thus reducing the profit margin. 1. Huge market demand for more efficient processor 2. Lower prices give better opportunities to penetrate into less developed markets 3. Contracts with Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) and reseller companies 1. Market dominance by Intel Need to respond accordingly to Intel’s action e.g. introduction of new processor or new technology – could lead to loss or pressure to release new products (could lead to prematurely developed product) 2. Rival Intel further price cuts Forces AMD to cut price as well, to stay competitive 3. Lawsuits -From competitor (Intel may sue the company for certain matters) -From government (Antitrust agency)