China Geography
advertisement
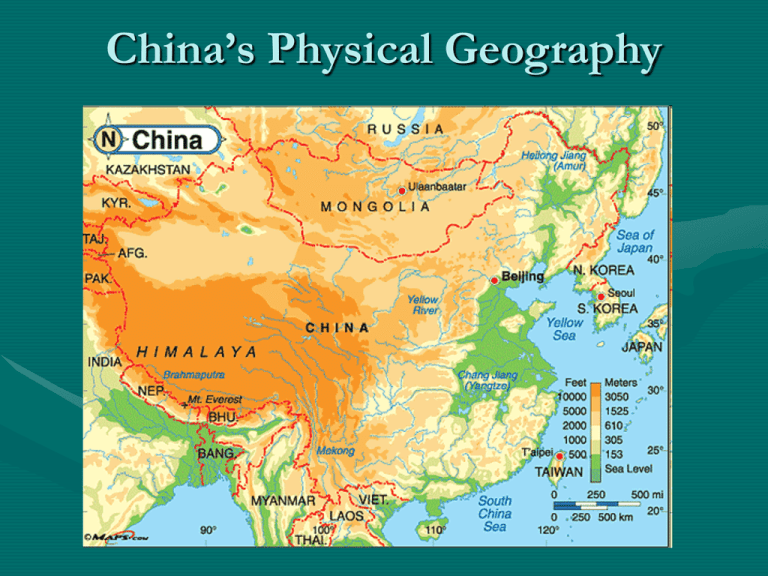
China’s Physical Geography Taklimakan Desert • Taklimakan Desert • Means, “Land of irrevocable death” • Vast, sandy desert • Located N.W. China – Kunlun Mountains (Sian) to south – Tian Sian and Tarim River to North • 105,000 square miles in central Tarim Basin • 984 ft. high sand dunes – Space needle 605ft – Columbia tower 967ft East China Sea • East China Sea • 290,000 square miles • Largely shallow with 71% less than 650ft deep • Average depth = 1,145Ft • Weather dominated by monsoon wind systems South China Sea • South China Sea • Covers 848,000 square miles • Located between S.E. Asian mainland and Taiwan, the Philippines and Borneo • S.W. part (from Gulf of Siam to Java Sea) is a submerged plain and generally shallow • N.E. part is deep basin – Depths up to 18,000 feet • Many islands dot sea Mount Everest • Mt. Everest • Chinese call Zhumulong Mafeng • On border of China and Nepal in central Himalayas. • 29,028 feet • Highest mountain in the world Tian Shan • Tian Shan • Shan mean “mountain” • 1,500 miles long from Pamir Mts through N.W. China to ChinaMongolian border • Dry climate so snow line is usually above 11,000 ft. • Coal, iron, lead, zinc are mined • Grains are main crop in valleys Turfan Depression • Turfan Depression • • • • • • • Also called Dzungarian Basin Fault trough 650km long Lowest point 505 ft below sea level Lowest point in China Intensely farmed Famous for grapes Melons, peaches, apricots, nuts, cotton, silk and wheat also produced Mekong River • Mekong River • 2,600 miles long • Headwaters in Tibetan Highlands, through Yunnan province, forms Myanmar (Burma)-Laos border, through Laos, to Cambodia, forming Mekong Delta (fertile region in Vietnam and spills into S. China Sea Catfish = 118 inches, 661.4 pounds North China Plain • North China Plain • • • • 135,000 square miles 2nd largest plain Flat and low (below 150 ft) River channels are higher than surrounding area • Highest proportion of land under cultivation in all of China Yellow River • Yellow River • Chinese call it Huang He • 3,000 miles long • Headwaters in Kunlun Mts. Flows east into Yellow Sea • Dry, winter season, river is slow and most of riverbed is empty • In summer, river rages out of control • Since 2nd century B.C, river has flooded over 1,500 times with 9 major course changes • Diverted once on purpose to stall Japanese invasion in 1938 Yangzi River • Yangzi River • Also Yangtze • Headwaters in Tibetan Highlands • Flows east for 3,450 mi • Flows through China’s middle basin – One of world’s most productive agricultural regions – One of world’s most populated regions • Long used as a major east-west trade and transportation route Gobi Desert • Gobi Desert • 1,000 mi. on plateau with area of 500,000 sq. mi • East to West across S.E. Mongolia and N. China • Grassy fringe supports small population of nomadic Mongolian sheep/camel herders • Fierce sand and wind storms common Yunnan Plateau • Yunnan Plateau • Eastern half is limestone contains canyonlike valleys, precipitous mts • Marked by numerous sinks, ravines, underground streams • Rugged terrain produces wide range of flora fauna Sichuan Basin • Sichuan Basin • • • • Also known as Red Basin One of most attractive regions 75,000 sq mi Surrounded by mountains – Protect is against cold and North winds in winter • Very hilly (except for Chengdu plain) • Little arable land so farmers must build terraces on slopes to grow crops
![Georgina Basin Factsheet [DOCX 1.4mb]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006607361_1-8840af865700fceb4b28253415797ba7-300x300.png)










