Relative Dating and Sequencing Notes
advertisement

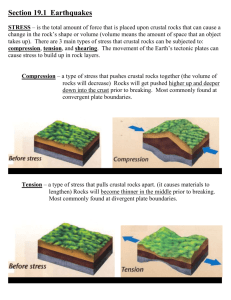
Relative Dating and Sequencing Notes! Relative Dating and Sequencing • • • • Relative vs. Absolute Time Laws Unconformities Correlating Geologic Cross Sections ________________: • Ages of events are placed in order of occurrence. • No exact date is identified. – Ex. WWI and WWII – I am the second child in my family. – Mr. Williams is mad old, yo _________________: • identifies the exact date of an event. – Ex. 65 Million Years Ago – 1990 Nicholas Steno • First Things First…or… “How’d that get there?” • In the 17th C., Nicolas Steno made an important observation: "Sediments are usually deposited in __________ layers." He called this “ORIGINAL _______________” 1. The Law of ______________ - in a sequence of undisturbed sedimentary rocks, the oldest rocks will be at the bottom. 2. The law of _________________ relationships – anything that cuts across layers of rock is younger than the rocks that it has intruded into. This applies to faults and igneous intrusions. 3. The law of ______________ fragments - the fragments that make up a rock are older than the entire sample. 4. The Law of _________or _______: tilts in rocks are younger than the rocks themselves. 5 The Law of Original ____________- Rocks are usually deposited flat and level. 6. Cole’s LawThinly sliced cabbage. Contact Metamorphism! • ___________________ shows that the rock that was changed was there first when the intrusion happened. Formation of an unconformity • An ___________________ is an old buried surface that was eroded • Over time, new rock layers were deposited on it • Sometimes layers of rock are missing • There is a break or gap of ______________ not represented by the layers in an area. The gap represents an unknown length of time • No way of knowing exactly what happened but we do know ____________ exposed rocks to weathering and erosion. • Rocks above unconformity are ______________ – rocks below _______ How is an unconformity formed? 1. ___________– area of crust uplifted above sea level (deposition – under water) 2. ___________ – some time after 3. ___________ (subsidence) below sea level 4. ___________ – new sediments deposited on top of the buried eroded surface