Coasts - WordPress.com

COASTS
The Coast is.........................
MASS MOVEMENT
• This is where the coastline is altered because of LAND processes.
1. Mudflow
2. Rockfall
MASS MOVEMENT
• This is where the coastline is altered because of LAND processes.
3. Landslide
4. Rotation Slip
Types of Weathering
1. Mechanical
Weathering:
Freeze – Thaw
• Rocks are broken down by the action of ice
2.Chemical Weathering
• This is called SOLUTION. As sugar dissolves in tea, some rocks dissolve in rainwater.
• Some alkaline rocks (chalk and limestone) are attacked by a process called
CARBONATION which is acidic rainfall dissolving them.
3. Biological Weathering
• This is where rocks are broken down by the action of burrowing animals and growing plants
• Roots of trees can create great pressure and rocks can be split apart
Coastal Processes: from the sea acting on the coast
Erosion
Transportation
Deposition
Types of Wave:
1) Destructive – results in features/landforms of erosion
Types of Wave:
2) Constructive – result in features/landforms of deposition
Forms of Coastal Erosion:
1. Corrasion – waves throw sand and pebbles at a cliff and wear it away.
2. Attrition – stones and pebbles smash into each other and break into small pieces, eventually becoming sand.
3. Solution – certain rock types (eg. chalk) react with sea water and dissolve.
4. Hydraulic Action – force of waves crashing into cliffs, air gets trapped in cracks making pressure which cracks the rock.
A process of Transportation –
Traction
Pebbles roll along the bottom of the sea bed.
A process of Transportation –
Saltation
Pebbles bounce on the bottom of the sea bed.
A process of Transportation –
Suspension
Smaller pebbles are carried in the water. Not touching the seabed.
A process of Transportation –
Solution
Particles are dissolved in the water and transported
Why do we get headlands and bays?
Bays
Headlands
Soft rock
Hard rock
Coastal Processes: from the sea acting on the coast
Erosion
Transportation
Deposition
Longshore Drift
Why was geology important in the formation of Lulworth cove?
Softest
Rock
Hardest
Rock
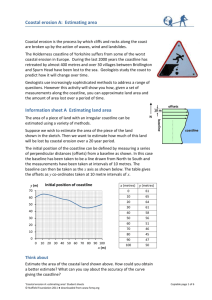
5
8
1
What coastal landforms can you get and how are they formed?
2
3 4
6 7
9 10
11
Features created by Erosion
Caves, Arches, Stacks and Stumps....
The sea, continues to erode the cave until the eroded from weathering and the bottom from falls in and results in a resulting in a stump
Headland
The Sea
Stack
Stump
What depositional landforms can you get and how are they formed?
Case Studies:
Coasts:
1. Impacts of Rising Sea level = The Maldives
2. Recent Cliff Collapse = Holderness Coastline
3. Coastal Management (Costs/Benefits) =
Holderness Coastline
4. Coastal Habitat with distinct Characteristics
= Keyhaven Salt Marsh, Hampshire
1. The Impacts of Rising Sea Level
THE MALDIVES
The Maldives
• 300 000 people
• 1190 islands, 80% of the land is 1m below sea level!
• Sea levels are rising by 0.9cm a year.
What is Global Warming?
What are the affects on coastlines?
What are the figures?
What is causing the rise?
Ice cap and Glacier melt
PLUS thermal expansion
Collapse of the West Antarctic ice sheet and Greenland could cause a 6 metre rise and could happen within a 100 years!!!! This image is a computer generated simulation of what could happen in the future to the UK…………………..
1. Loss of
Tourism
4. Buying land in other countries
6. Houses destroyed
2. Loss of beaches
3. Loss of
Coral Reefs
The IMPACTS of rising sea level
7. Loss of
Soil
Which are:
• Economic
5. Disrupted fishing industry
8.Asking for aid
1. Loss of
Tourism
4. Buying land in other countries
6. Houses destroyed
2. Loss of beaches
3. Loss of
Coral Reefs
The IMPACTS of rising sea level
7. Loss of
Soil
Which are:
• Economic
5. Disrupted fishing industry
8.Asking for aid
1. Loss of
Tourism
4. Buying land in other countries
6. Houses destroyed
2. Loss of beaches
3. Loss of
Coral Reefs
The IMPACTS of rising sea level
7. Loss of
Soil
Which are:
• Environmental?
5. Disrupted fishing industry
8.Asking for aid
1. Loss of
Tourism
4. Buying land in other countries
6. Houses destroyed
2. Loss of beaches
3. Loss of
Coral Reefs
The IMPACTS of rising sea level
7. Loss of
Soil
Which are:
• Environmental?
5. Disrupted fishing industry
8.Asking for aid
1. Loss of
Tourism
4. Buying land in other countries
6. Houses destroyed
2. Loss of beaches
3. Loss of
Coral Reefs
The IMPACTS of rising sea level
7. Loss of
Soil
Which are:
• Social?
5. Disrupted fishing industry
8.Asking for aid
1. Loss of
Tourism
4. Buying land in other countries
6. Houses destroyed
2. Loss of beaches
3. Loss of
Coral Reefs
The IMPACTS of rising sea level
7. Loss of
Soil
Which are:
• Social?
5. Disrupted fishing industry
8.Asking for aid
Case Studies:
Coasts:
1. Impacts of Rising Sea level = The Maldives
2. Recent Cliff Collapse = Holderness Coastline
3. Coastal Management (Costs/Benefits) =
Holderness Coastline
4. Coastal Habitat with distinct Characteristics
= Keyhaven Salt Marsh, Hampshire
LO1: To know what management strategies there are
Guess The Coastal Management
LO1: To know what management strategies there are
Guess The Coastal Management
LO1: To know what management strategies there are
A
Hard or Soft?
1. Match up the defence with their names
2. Are they are Hard or Soft forms of engineering
8. Revetment
D
H
C
B
F
G
E
Which form of coastal management is the most sustainable?
Think about Economically (Money), Environmentally (Natural Environment) and Socially (People)
Sea Wall
Cost: £3,500-5,000 per Metre
Lifespan: 100 years
Gabions
Cost: £1,000 perM3
Lifespan: 10 Years
Beach Replenishment
Cost: £5,000-200,000 per 100m
Lifespan: 1-10 years.
Wooden Groynes
Cost: £1,000 per M
Lifespan: 30-40 Years
2&3. The Holderness Coastline:
Cliff Collapse and Coastal Management
A case study to show an area of cliff collapse- rates of erosion, reasons why some areas are susceptible, how people may make the situation worse, impacts on people’s lives and the environment
2m lost a year!!!
Unstable cliffs can often collapse if they are undercut by wave action, weathering, or are susceptible to mass movement
As a result of the landslide the edge of the cliff recedes.
2&3. The Holderness Coastline:
Cliff Collapse and Coastal Management
The costs and benefits of coastal management
Mappleton:
• 50 Properties
• 2m a year lost
• Access road only 50m from the coast now!
Geology:
• Areas rock is Till (Very soft!)
Management:
• 1991
£2million on 2 x Rock Groynes and a rock revetment
These created a beach, reducing erosion.
HOWEVER…. Down coast erosion has
INCREASED!! Even on a neap time (30% lower than a normal tide) the waves reach the cliffs and erode them!!
What else is causing the erosion apart from Geology?
Businesses lost or under threat.
Farmland Eroded
House Prices
Reduced,
Insurance companies wont pay out
Homeowners wont get insurance OR it will be
VERY expensive Loss of homes at
Withernsea
Use a Case Study to describe the effects of coastal flooding (4 Marks)
Explain why areas such as Lyme
Regis use both hard and soft engineering strategies
(8 Marks)
Case Studies:
Coasts:
1. Impacts of Rising Sea level = The Maldives
2. Recent Cliff Collapse = Holderness Coastline
3. Coastal Management (Costs/Benefits) =
Holderness Coastline
4. Coastal Habitat with distinct Characteristics
= Keyhaven Salt Marsh, Hampshire
4. Keyhaven Salt Marsh, Hampshire
A coastal habitat with distinct characteristics
• How its been formed
• Its features
• What plants and animal species are there
• Ways to conserve sustainably whilst still using the area
Hurst Castle Spit
Keyhaven Salt
Marsh
Oyster Catcher
Cordgrass
Wold Spider
Sea Lavender
Ringed Plover
How are these suited to life on the spit?
Conservation and Sustainable Use
• What pressures does the salt marsh face?
– Sea Level rise and Climate change causing severe storms and flooding. (Loss of 6m a year)
– Breaching of the spit (1989)
• How will it be conserved?
– 1996 (£5 million) Rip Rap
Installed and Beach
Nourishment
– Protected by SSSI status – acess and development limited
Use a Case Study to explain why a coastal habitat has distinct characteristics
(8 Marks)
Using a case study, discuss the effects of cliff collapse on peoples lives and the environment
(8 Marks)