crowded coasts 10 - SLC Geog A Level Blog
advertisement

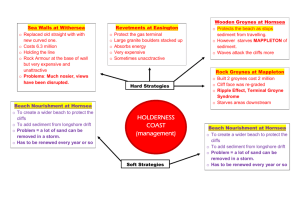
Coastal Management- strategies along a stretch of coastline •Explain how the coastline is divided up to make management easier. •Describe the methods used to prevent coastal erosion and divide these into traditional and modern types and also hard and soft engineering methods. •Evaluate the efficiency of each method and identify advantages and disadvantages of each method. •Describe the management system in place for a named stretch of the UK Coast Starter Risks of rapid coastal erosion in Holderness Can we protect the entire coast of the UK or elsewhere? 1. How do we decide where needs protection? 2. How do we decide what level of protection to give to a place? 3. What happens to places that we don’t protect? 4. Who organises the protection of the coast? What methods can we use to protect the coast? CLIFF FOOT AND BEACH STRATEGIES Technique Nature & Purpose Breakwaters offshore Embankments Gabions Groynes Revetments Rip Rap (Rock Armour) Sea walls CLIFF FACE STRATEGIES Cliff drainage Cliff fixing Cliff regrading Beach nourishment Beach re-profiling Dune regeneration Developing natural defences of coral reefs and mangroves Offshore reefs Ref Phillip Allan 240 -242 Strengths Weaknesses Breakwaters Offshore Embankments Gabions Groynes Revetments Rip Rap / Sea wall Straight sea wall Recurved sea wall Cliff drainage Cliff fixing Cliff regrading Beach nourishment Beach re-profiling Dune regeneration Developing natural defences of coral reefs and mangroves Offshore reefs Soft and hard engineering • What is the difference between hard and soft engineering management schemes? • Does soft engineering appeal simply on cost? Justify? Integrated coastal zone management (ICZM) & Shoreline Management Plans (SMP) • This means that rather than sections of the coast being managed by individual towns or villages, they are managed as a whole • Realisation that acting in one place affects other places along coastline i.e. Mappleton. • Due to sediments cells Sediment Cells Read p194 of Phillip Allan and p194 Pearson and Holderness photocopy (Oxford). • Produce a short paragraph explaining what a sediment cell is. • Produce a simple sketch map of England showing the 11 sediment cells. • How is an understanding of sediment cells essential if the principles of shoreline management plans are to work? Shoreline Management Plans (SMP) • In a SMP all local interest groups are consulted and provide engineers with background information about that stretch of coast – 4 options considered • DO NOTHING – i.e. let existing defences collapse • HOLD THE LINE i.e. keep the coastline where it is by using hard engineering (Sheringham) • ADVANCE THE LINE i.e. build coastal defences out to sea i.e. artificial breakwaters (Dubai) • RETREAT THE LINE i.e. allow the coast to erode back to a defined line (South of Mapleton) SMP • Cost benefit analysis and environmental impact analysis (EIA) carried out to decide best option • SMP can be valid for up to 50 years • Unprotected areas eventually erode inland and protected areas form small headlands – alters shape of coast into series of bays. Case Study – Coastal defences on the Holderness coast. • • • • Identify coastal defences in place at three locations along Holderness coast: Withernsea, Mappleton and Flamborough Describe how each method works and outline advantages and disadvantages for each technique suggesting where appropriate whether another technique would be better. Also use Google maps to find an area of the Holderness coast where no defences are present and to examine why this would be the case. Use the sheet provided to study and evaluate the coastal defences in place along the Holderness coast. Ref Oxford 198-201, Plenary • Arguments for and against coastline retreat? • Why are sediment cells so important in coastal management?