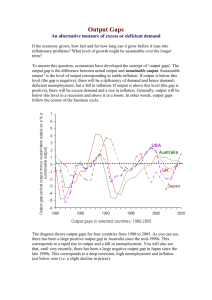
File

A Keynes vs Monetarist view
Looks at the role that fiscal policy can play in stabilizing the economy.
Keynesian theory suggests that higher government spending in a recession can help the economy recover quicker.
Keynesians say it is a mistake to wait for markets to clear like classical economic theory suggests
In a recession, people responded to the threat of unemployment by
increasing saving
& reducing spending
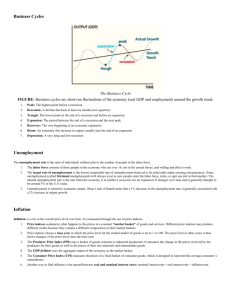
RECESSION
Government intervention
STIMULATES AD and REAL GDP
What about
Policy Tools?
Which ones can be used to stimulate AD
Wages may be ‘sticky downward’/ inflexible
’
Workers do not accept nominal wage cuts
,
Firms have to lay off workers
This can lead to involuntary unemployment.
The economy slows down
In a recession, an economy has spare capacity,
SO: increasing AD will have an impact on real output and only minimal effect on the price level
.
INCREASE SPENDING
(
C + I + G + X – M).
Keynesians believe there is a multiplier effect
This means
an initial injection (eg increased government spending) into the circular flow can lead to a bigger final increase in real GDP
“It is more important to reduce unemployment than inflation”
Keynesians support expansionary fiscal policy in a recession.
Keynesians reject real business cycle theories
(an idea that the government can have no influence over the economic cycle)
WHAT does this mean???
•
•
•
•
The economy is naturally stable.
Markets work well when left to themselves.
Government interference can weaken the economy
Fiscal Policy is often bad policy.
A small role for government is good.
Monetarists stress the importance of
controlling the money supply
to keep inflation low
Focus on MONETARY POLICY TOOLS which increase or decrease the supply of money and credit.
MV=PQ
IN THE SHORT RUN velocity is stable. This implies that in the short run, changes in the money supply are the dominant forces that change nominal GDP.
MV=PQ)
IN THE LONG RUN the economy is at potential output, so changes in the money supply only lead to higher prices, not higher output
SHORT RUN?
LONG RUN?
SHOW THE DIFFENCE BY DRAWING THE AD/AS GRAPHS.
Monetarists stress the role of the natural rate of unemployment (supply side unemployment)
MONETARISTS say … “REDUCE INFLATION”
Monetarists more likely to place emphasis on reducing inflation than keeping unemployment low
"Inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon."
REGULATOR?
POLICY ?
POLICY TOOLS?
AD?
AS?
GRAPH(S)
KEYNESIAN MONETARIST