Chapter 4
advertisement

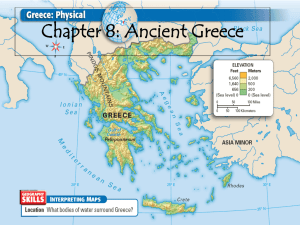
Chapter 4 The Early Greeks Geography of Greece How did geography affect the Greek way of life? The geography of Greece influenced where people settled and what they did. -Jobs: fishers, sailors, and traders -Farming: grew wheat, barley, olives, grapes; raised sheep and goats. -Transportation -Relationships How did geography discourage Greek unity? The mountains and seas kept them apart and encouraged independence. Bull Jumping The Minoans Who were the Minoans? Arthur Evans discovered the ruins of a palace that had been the center of Minoan civilization. They were not Greeks, but were the first to live in the region later known as Greece. Artifacts at the palace at Knossos reveal the riches of the Minoan people, such as wine, oil, jewelry, and statues. The Minoans became a great sea trader. Collapsed in 1450 B.C. , but historians argue over the real reason of their destruction. First Greek Kingdoms Who were the Mycenaean's? Some historians believed they conquered the Minoan civilization. Became the first Greek kings and lived in fortified palaces, surrounded by the nobles’ estates. Government officials kept track of people’s wealth and collected wheat, livestock, and honey as taxes and stored them in the palace. How did the Minoans influence the people of Mycenae? Minoans visited and the Mycenaean’s copied many of their ways, such as worshiping the same god, using the sun and stars to find their way at sea, working with bronze, and building ships. What was their greatest victory? King Agamemnon led the Mycenaean's to victory in the Trojan War. What was the Dark Age? What changes occurred during the Dark Age? Earthquakes and fighting destroyed hilltop forts. Farmers only grew enough food for their families. People stopped teaching others how to write and do crafts. Huge population shift occurred during this time, which helped spread the Greek culture. Dorians invaded Greece on the Peloponnesus peninsula and brought iron weapons with them. Farming and trade eventually increased, and the development of the alphabet helped spread ideas. A Move to Colonize How did new colonies affect industry? Farmers could no longer grow enough grain to feed everyone, so people were sent out to develop colonies . Greek cultures spread as colonies were set up along the coasts of Italy, France, Spain, North Africa, and western Asia. The Greeks began to mint coins, so they were able to trade for money rather than other goods. People began to specialize in certain products from their area as the demand grew, which led to the growth of industry. The Polis What were Greek city states called and how were they organized? Each Greek city-state was known as a polis. There was an acropolis, which was a fortified area that provided safety during attacks, that was built on top of a hill in the center of the polis. An open area called an agora was used for both a market and a debate area. City-states could be small or large. One of the largest was Athens, which had over 300,000 people in 500 B.C. Greek citizenship What was Greek citizenship? Citizens are people who are part of a political community who treat each others as equals and who have rights and responsibilities. Greek citizenship was a new idea, as most people in ancient Mesopotamia and Egypt had no say in government matters. -Only native born men could be citizens -Women and slaves were citizens but had no rights What were the rights of Greek citizens? 1) They could gather in the agora to choose officials and pass laws. 2) Vote 3) Hold office 4) Own property 5) Defend themselves in court Citizens as Soldiers How did citizenship make the Greeks different from other ancient people? Citizenship changed the way battles were fought. Instead of nobles fighting on horseback, ordinary citizens called hoplites fought. Hoplites couldn’t afford horses, so they went into battle on foot and heavily armed. -Row upon row, shoulder to shoulder Hoplites were very loyal to their citystate but very distrustful of other poleis. WIO 2nd, 3rd period– Review Sections 1 and 2 of the Fourteenth Amendment of the U.S. Constitution. Answer these questions: 1) How does Section 1 define citizenship? 2) What rights are guaranteed to citizens? HOMEWORK: Compare the rights associated in ancient Greece with those in the U.S. and decide which are more inclusive. Post your thoughts on the message board. You must have at least five to seven sentences. 1st, 4th, 6th - Review the way the hoplites fought and picture that in your mind. Do you think this is an effective way to go into battle? Why or why not? 14th Amendment • Section 1.All persons born or naturalized in the United States, and subject to the jurisdiction thereof, are citizens of the United States and of the state wherein they reside. No state shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any state deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws. • Section 2.Representatives shall be apportioned among the several states according to their respective numbers, counting the whole number of persons in each state, excluding Indians not taxed. But when the right to vote at any election for the choice of electors for President and Vice President of the United States, Representatives in Congress, the executive and judicial officers of a state, or the members of the legislature thereof, is denied to any of the male inhabitants of such state, being twenty-one years of age, and citizens of the United States, or in any way abridged, except for participation in rebellion, or other crime, the basis of representation therein shall be reduced in the proportion which the number of such male citizens shall bear to the whole number of male citizens twenty-one years of age in such state. • http://topics.law.cornell.edu/constitution/amendmentxiv