Tidal & Wave Power
advertisement

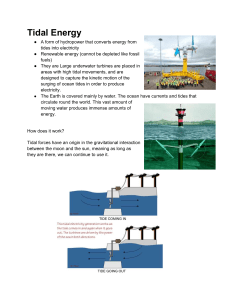
Tidal & Wave Power Andrew Chavous & Carlo Raiteri Tides Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon and the Sun and the rotation of the Earth. What is Tidal Energy Tidal power, also called tidal energy, is a form of hydropower that converts the energy of tides into useful forms of power - mainly electricity. This is the only form of energy whose source is the moon. History of Tidal Energy Tide mills are one of the oldest forms of energy 787 A.D. on Spanish, French and British coasts The incoming water was contained in large storage ponds, and as the tide went out it turned waterwheels producing mechanical power to mill grain 19th century – Process of using Tidal Power to create electricity was introduced in U.S. and Europe 1966 – First large-scale tidal power plant was built in France Examples of Tidal Energy Generation Tidal Barrage Tidal Streams (turbines) Tidal Lagoons Tidal Barrage The Rance tidal barrage in North-West France is one of the largest in the world Tidal Streams Make use of the kinetic energy of moving water to power turbines in a similar way to wind turbines that use wind to power turbines Tidal Lagoons Pros & Cons of Tidal Energy PROS CONS Consistent Power Marine Life Affected Pollution-Free High Initial Cost Low Operating Costs Device Breakdown Renewable Only provides power for around 10 hrs Efficient Few suitable sites for tidal barrages Tides are predictable Locations are often remote Impacts are local not global May restrict access to open water Provide a storm surge barrier Can change tidal levels Decreases salinity in tidal basins Captures waste near the coast Reduces kinetic energy of the ocean Future of Tidal Energy Potential for future electricity generation Tides are more predictable than wind and solar energy. Many recent technological developments and improvements, both in design and turbine technology, indicate that the total availability of tidal power may be much higher than previously assumed Economic and environmental costs may be brought down to competitive levels. Wave Energy Wave power devices take energy directly from surface waves or from pressure fluctuations below the surface. Wave power is of course powered by waves. As a wave goes by, the buoy rotates and transforms mechanical energy into electrical energy. History of Wave Energy First patent to use energy converted from waves dates back to 1799 in Paris. From 1855 to 1973 there was a drastic increase in exploring potential of wave energy, as 340 patents were filed in England alone. During the 1970's gasoline crisis, wave power was pushed in order to be a good long term energy solution. Later, the energy crisis was resolved yet the leaps and bounds made in the innovation of wave power remained. 2008 – First experimental wave farm opened in Portugal Example of Wave Energy Pros & Cons of Wave Energy PROS Consistent Power Pollution Free Low Operating Cost Renewable Minimal Visual Impact Efficient Shoreline Protection Enormous Energy Potential Offshore Wave Power CONS Marine Life Effected (not sure) Device Breakdown High Initial Cost Few Implemented Early Stages of Development Future of Wave Energy Wave power has an enormous global potential. We need more funding and research to polish the technology involved, pushing prices down to a competitive level. Price for generating energy from ocean waves is still about twice as high as that of wind energy.