Renewable Energy School Presentation
advertisement

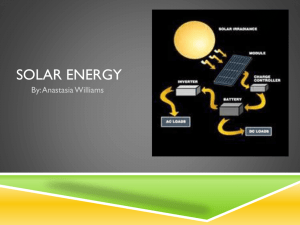
Renewable Energy Growth that doesn’t cost the earth. www.resourceefficientscotland.com Wind Energy • Wind turbines turn wind energy into electricity • and is a potentially infinite energy supply. • The best turbine design is a tall tower with three blades. • The wind makes the blades spin. The moving blades create electricity. • They are usually built in groups called wind farms. Whitelee Wind Farm UK's largest onshore wind farm, located south of Glasgow. Its 215 turbines generate enough to power just under 300,000 homes. Growth that doesn’t cost the earth. www.resourceefficientscotland.com Wave Energy • Waves are a result of the effects of wind on the oceans and seas. • Waves are not as consistent as the tide and therefore there can cause issues trying to match the UK’s supply and demand for power. • Wave power tends to be small scale schemes rather than large scale commercial plant. Wave Energy There are different types of wave energy collectors. One of the systems is called the Oscillating Water Column. It uses the movement of the seawater in and out to compress the trapped air, which then drives a turbine and creates energy. There is currently a device generating and supplying 0.5MW of power to the grid on the Island of Islay off the west coast. Wave Energy Another system is called the Hinged Contour Device. This snake like device moves with the waves. The wave movement causes pressure within different sections of the device which then drives the motors, generating electricity. Theses devices are currently being developed and tested in Scotland. Tidal Energy • Tidal Energy is generated from the movement of the tides in and out which drives turbines. • A tidal barrage (a kind of dam) can be built across an estuaries which forces the water through the gaps. • A tidal barrage can double as bridge, and can help prevent flooding. • Construction of barrage is very costly. • Not all estuaries are suitable. Biomass • Biomass fuels come from organic materials, primarily wood. • Biomass can be a long-term, sustainable energy source. • It is a cheaper and more readily available source of energy. • Wood can be chipped or made into wood pellets Photovoltaics • Solar cells are devices that convert light energy directly into electrical energy. • Panels absorb solar rays of heat and light. • Potentially infinite energy supply. • Single dwellings can have own electricity supply • Manufacture and implementation of solar panels can be costly. • Larger arrays of solar cells are used to power road signs, and even larger arrays are used to power satellites in orbit around Earth. Solar Panels • Solar panels are different to solar cells. • Solar panels do not generate electricity. Instead they heat up water directly. • A pump pushes cold water from a storage tank through pipes in the solar panel. • The water is heated by absorbing energy from the sun and returns to the tank. • They are often located on the roofs of buildings where they can receive the most sunlight. Ground Source Heat Pumps The heat of the earth warms pipes of water buried underground. Hydro Power • Hydroelectric power schemes store water high up in dams. • The water has gravitational potential energy which is released when it falls. • As the water rushes down through pipes, this stored energy is transferred to kinetic energy, which turns electricity generators. • Creates water reserves as well as energy supplies. • Dams have major ecological impacts on local hydrology.