The Great War
advertisement

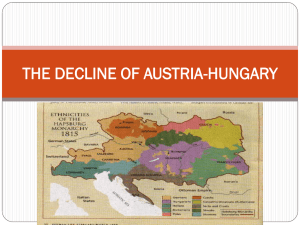
World War I Glencoe World History Chapter 23 SSWH16 The student will demonstrate an understanding of long-term causes of World War I and its global impact. a. Identify the causes of the war; include Balkan nationalism, entangling alliances, and militarism. b. Describe conditions on the war front for soldiers; include the Battle of Verdun. c. Explain the major decisions made in the Versailles Treaty; include German reparations and the mandate system that replaced Ottoman control. d. Analyze the destabilization of Europe in the collapse of the great empires; include the Romanov and Hapsburg dynasties. Causes of WWI Nationalism – Thought this would lead to cooperation?!?!?! Entangling Alliances – Triple Alliance (1882) Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy – Triple Entente (1907) France, Great Britain, and Russia Militarism – aggressive preparation for war – Growth of mass armies – After 1900 draft present in most European countries The Spark that led to War June 28, 1914- A member of a Serbian terrorist organization, Gavrilo Princip, assassinated the Archduke Francis Ferdinand and his wife Sophie Archduke Francis Ferdinand was the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne States in Southeast Europe had been struggling for many years to free themselves from Ottoman rule Serbia wanted a large Slavic state in the Balkans; Austria-Hungary determined this was NOT happening The Spark that led to War Austria Hungary made harsh demands which Serbia refused to meet. July 28, 1914- Austria Hungary along with its ally, Germany, declared war on Serbia, who was supported by its ally, Russia. Within a week, Austria Hungary and Germany were at war with Russia, France, and Great Britain Before the war ended, 30 countries on six continents would be involved Two Sides Central Powers – Austria Hungary – Germany – Ottoman Empire Allied Powers (Allies) – France – Russia – Great Britain – Italy (joined in 1915) Western Front Germany hoped for a quick end to the war Germany stopped at the First Battle of the Marne 600 mile line from the Swiss border to the English Channel Western Front No man’s land~ area in between the trenches Thousands died, no one able to break through enemy line or end the trench warfare Eastern Front Marked by mobility Russians faced enormous losses – 2.5 million Russians killed, captured, or wounded Germany, Austria-Hungary, and ally Bulgaria eliminated Serbia and moved to the Western Front Italy betrayed Germany by attacking Austria in May 1915 Conditions on the Warfront Generals did not know how to deal with trench warfare in west During 1916 and 1917 millions died in search of the elusive break through In 1916, in 10 months at Verdun, France, 700,000 men lost their lives over a few miles of land War of attrition Living in holes in the ground Decomposing bodies, rats, etc… Military Situation in 1917 By 1917, Allies had faced enormous losses Allied offensives on the Western front had been badly defeated Tsar of Russia deposed and new government established- Bolsheviks (Communists) Russian Revolution in November 1917, led to their withdrawal a few months later ceding territory to Germany American entry a bright spot to a bleak year – Provided a much need psychological boost – Fresh men – Fresh material Germany’s Last Bid for Victory March 1918~ Germany launched a powerful campaign to end the war By April, they were 50 miles from Paris July 18, German advance stopped at the Second Battle of the Marne by a combined force of French, Moroccan, and American troops supported by tanks World War I Map Activity Paris Peace Conference January 1919 27 victorious allied nations met to make a final settlement but there were problems… – Secret treaties (Territories, Reparation Payments, etc…) – National interests – Germany not invited to defend themselves – Russia in a civil war and could not come Big Four Great Britain – Prime Minister David Lloyd George – Elected on platform “Make Germany Pay” France – Premier Georges Clemenceau – Wanted national security from Germany invasion & revenge Italy – Vittorio Orlando- Smaller role than the big three powers The United States – President Woodrow Wilson – Wanted lasting peace… compromised believing the League of Nations would fix any unfair settlements; Senate refused to ratify the agreement Treaty of Versailles Late June 1919, final peace treaty signed 5 separate treaties with Germany, Austria, Hungary, Bulgaria, and Turkey Germany is the most significant – Germany responsible for starting war – Must pay reparations for all the damage to the Allied countries – Reduce army, navy and eliminate Air Force – Zone was completely demilitarized – Alsace & Lorraine returned to France Results of the Treaties Ottoman Empire broken up Poland recreated from sections of East Germany Austro-Hungarian empire disappeared Czechoslovakia, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and Yugoslavia were created (from former Austro-Hungarian Empire) Mandate System To gain support of Arab states in the Ottoman Empire, West promised them independence, but changed their minds after the war… Mandate system developed- a nation officially governed another nation on behalf of the League of Nations but did not own the territory France- Lebanon & Syria Great Britain- Iraq and Palestine Impact Death of almost 10 million people Revolutions broke up old empires (Russian Revolution- Romanov dynasty and the Hapsburg dynasty in the Austro-Hungarian empire) and created new states Power of governments increased; strong central authority a way of life Communism became a factor in global conflict as other nations turned to its ideology.