TAV Chapter 2
advertisement

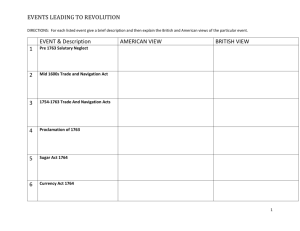
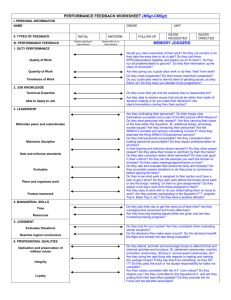
TAV Chapter 2 The American Revolution Section 1 Colonies Fight for their Rights The French and Indian War • Struggle over the Ohio River Valley • 1754, Washington • Fort Necessity The Albany Conference • 7 colonies met w. the leaders of the Iroquois in Albany, NY in June 1754. • Iroquois controlled western NY where the French would have to go to get to the Ohio River. • Iroquois promised neutrality • Albany Plan of Union -Ben Franklin – Proposed that the colonies form a Fed. Govt.rejected British Triumph • 1755, Gen. Edward Braddock was killed in an ambush about 7 miles from Ft. Duquesne • Washington was Braddock’s aid • 1756 fighting erupts in Europe • Fall of Quebec • 1763 Treaty of Paris signed • Britain won but was deep in debt Proclamation of 1763 • Pontiac was still at war w. GB • Oct 1763, King George issues the proclamation • Fighting w. Pontiac ends late in 1765. • Oct 10, 1765 GB finally takes control of the land won during the French and Indian War – Thomas Sterling Customs Reforms • 1763 George Grenville became prime minister and wanted to stop smuggling in order to collect taxes on goods being shipped • End of salutary neglect • Smugglers to be tried in Nova Scotia – John Hancock defended by John Adams Sugar Act 1764 • Aka American Revenue Act – Sugar, molasses, and other goods • Began the cry of, “No taxation without representation.” • Currency Act of 1764, was to curb inflation – Banned the use of paper money in the colonies Stamp Act of 1765 • Taxed printed goods and documents • Led to the formation of the Sons of Liberty • Stamp Act Congress – Declaration of Rights and Grievances • Boycott – Nonimportation Agreement • Repealed in 1766 Townshend Acts • Revenue Act of 1767 • Glass, lead, and tea Boston Massacre • March 5, 1770 Chapter 2 Section 2 THE REVOLUTION BEGINS The Gaspee Affair • June 1772 the Gaspee ran aground The Boston Tea Party • Dec. 17, 1773 Coercive Acts • • • • Port Bill Massachusetts Government Act Administration of Justice Act Quartering Act – 2,000 troops – Gen. Thomas Gage as Gov. of Massachusetts Terms • Minutemen • Loyalists-Tories • Patriots Lexington & Concord • April 18, 1775 • 700 Redcoats march to Concord to seize rebel supplies. • Lexington Green 70 Minutemen stand in the way – 8 killed • GB lost 99 men w. 174 wounded • Patriots lost 49 w. 46 wounded Battle of Bunker Hill • June 17, 1775, British attacked 3 times in order to finally take the hill Olive Branch Petition • July 1775, the Continental Congress sent a letter to King George III asking to cease the fighting. • Attacks on Montreal and Quebec convinced the King that the colonists were not really serious about reconciliation. Common Sense • Thomas Paine • Pamphlet that identified the king as a tyrant • Many who were unsure began to side with the Patriots after reading Common Sense. INDEPENDENCE • July 4, 1776 • Thomas Jefferson Chapter 2 Section 3 THE WAR FOR INDEPENDENCE Numbers • General Howe had 32,000 troops • Washington had around 230,000 that served – No more than around 20,000 at any one time. • Advantages/Disadvantages Trenton / Princeton • Dec. 25, 1776 Washington leads 2,400 men across the Delaware R. in a surprise attack on Hessian soldiers. • Later they attack nearby Princeton • Retreat for the winter into the hills of New Jersey Fall of Philadelphia • March 1777 the British set up plans to take out the Continental Congress • Howe takes Philadelphia but w.out the desired affects. • Cont. Army winters in Valley Forge, PA. -2,500 men • Marquis de Lafayette and Baron Friedrich von Steuben train Cont. Army Saratoga • Oct. 17, 1777 British troops surrender around 5,000 troops • Led the French to enter the war on the side of the Americans • Nathan Hale • John Paul Jones – Richard Bonhomme vs Serapis • Francis Marion Yorktown • April 1781, General Cornwallis marched into Virginia in an attempt to win the war before more French troops arrived • Sept 28 Yorktown surrounded • Oct 19 the British surrendered 8,000 troops Treaty of Paris 1783 • Signed Sept. 3, 1783 • Nov. 24, the last British troops leave New York Chapter 2 Section 4 THE WAR CHANGES AMERICAN SOCIETY Republic • People elect others to act in their place • The people choose their representatives in Govt.