Science Project - Wikispaces - rms
advertisement

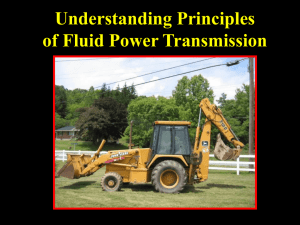
By: Emma Milburn & Samantha McMahon Hydraulics Hydraulics Hydraulics is the liquid version of pneumatics. In fluid power, hydraulics is used for the generation, control & transmission of power by the use of pressurized liquids. This covers concepts such as pipe flow, dam design, fluidics, and fluid control circuitry, pumps, turbines, hydropower, computational fluid dynamics, flow measurement, river channel behavior, and erosion. What are 4 hydraulic devices? Backhoes Bulldozers Car Crushers Jaws of Life How do hydraulic systems work? The hydraulic system is quite simple. Force that is applied to one point is transmitted to another point using an incompressible fluid. The force is almost always multiplied in the process. The brakes in your car are a good example of a piston-driven hydraulic system. Pneumatics Pneumatics Pneumatics is the use of pressurized gases to produce mechanical motions. Pneumatic systems are used in industry & factories extensively. What are 4 pneumatic devices? Air Compressors Paint Spray Equipment Sanders Buffers How do pneumatic systems work? Pneumatic systems are similar to hydraulic systems, with the same idea. But hydraulic systems use incompressible fluid, while pneumatic systems use compressible air. Filtered air is pulled through system by a vacuum pump. Evacuated air passes through the instrument case which causes gyro to spin. Spinning gyros provide 'rigidity in space' for instrument references. Air exhausts through the Gyro pressure gauge exhaust port. What are the major differences between hydraulics and pneumatics? Hydraulic systems use incompressible fluid, while pneumatic systems use compressible air. Particle Theory U.M.A.S.H U – Unique M – Movement A – Attraction S – Small H - Heat Unique All particles are unique. Movement All particles move. The faster the particles move, the more heat they produce. The slower the particles move, the more cold they produce. Attraction All particles attract each other, some more than others. Small All particles are small. Heat When particles move together fast they make heat. Particle Theory All matter is made up of invisible, tiny particles. Particles have spaces in between them. Particles are moving all the time. Particles move faster when they are heated. Particles attract each other Bibliography http://www.instruction.greenriver.edu/aviation/downl oads/AVIA112_files/Pneumatics.pdf http://answers.yahoo.com/question/index?qid=20070 428043812AACPWaG http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydraulics