Age of Exploration, Discovery, and Expansion
advertisement

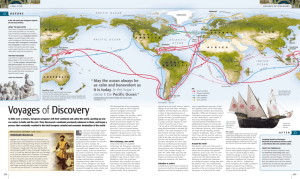
Age of Exploration, Discovery, and Expansion WH Standard 10- Analyze the impact of the age of discovery & expansion in the Americas, Africa, and Asia Motives and Means • The dynamic energy of Western civilization between 1500 and 1800 was most apparent when Europeans began to expand into the rest of the world • Economic motives loom large in European expansion. • Europeans hoped for spices & precious metals. Means and Motives Continued… • Another reason for the overseas voyages: religious zeal. Many shared the belief of Hernan Cortes that the natives are introduced into the Catholic faith. • They wanted to convert the natives to Christianity, but grandeur, glory, and a spirit of adventure also played a major role. • God, Glory, and Gold were the chief motives for exploration. Portuguese Trading Empire • The Portuguese took the lead in European expansion. • Beginning in 1420, Portuguese fleets began probing southward along the western coast of Africa. • There they discovered gold. Vasco da Gama (1460 – 1524) • In 1497, Vasco da Gama went around the Cape of Good Hope and cut across the Indian Ocean to the coast of India. • He took on a cargo of spices which he sold in Portugal for a profit of several thousand percent. • His arrival spelled the end of independence for the Swahili cities and led to the cities’ economic decline. Vasco da Gama Voyages to the Americas • The Portuguese sailed eastward through the Indian Ocean to reach the spice trade, while the Spanish sailed westward through the Atlantic Ocean. Christopher Columbus • Map maker • Very knowledgeable of the sea • Deeply religious • Believed he had found small islands off the coast of Asia Christopher Columbus • (1451 – 1506) • Italian, but sailed for King Ferdinand & Queen Isabella of Spain • October 1492 he reached the Americas where he explored the coastline of Cuba and the island of Hispaniola. • Throughout his life, He believed he had reached Asia when he actually reached all the major islands of the Caribbean and Honduras in Central America- all of which he called the Indies. Ferdinand Magellan • 1480 – 1521 • Portuguese Explorer • Set sail September 20, 1519 with a crew of 250 Spanish men • November 1520, Magellan passed through a narrow waterway, later named the Strait of Magellan, and emerged in the Pacific Ocean which he called the Pacific Sea. • Killed in the Philippines by the native peoples. Ferdinand Magellan • Remembered as the first person to sail around the world. • Although he did not make the full trip, one of his ships did. • The Philippines would become a major base for trade across Asia. James Cook (1728 – 1779) • English explorer, navigator, and captain of the HMS Endeavour. • April 1770 dropped anchor ten miles south of Sydney, Australia. • August 21 formally claimed the entire land for King George III. • Cook called the land New South Wales. • In accepting possession, the British completely ignored the native peoples. • The British established a penal colony in 1788 in Australia. James Cook Samuel de Champlain (1567 – 1635) • Sailed down the St. Lawrence River • In 1608, he founded Quebec, the first permanent French settlement in the Americas. • Meanwhile, the British were founding Virginia. Zheng He (1371 – 1433) • Visited the Western • A Court official sent Coast of India and the on a series of naval city states of East Africa. voyages into the Indian Ocean that • Returned with items sailed as far as the unknown to China such eastern coast of as giraffes which were Africa. placed in the Imperial Zoo. • 7 voyages between 1405 and 1433. • Voyages led to enormous profit but were halted • The largest ship was after Emperor Yong Le’s over 440 ft. long; death, never to be Columbus’ Santa revived. Maria was only 75 feet long! Zheng He A statue honoring Zheng He in Malaysia . Role of Conquistadors & Explorers • • • • • Conquistadors – Spanish conquerors Establish trading posts Establish colonies Bring back items their country does not have Spread their religion to the natives • Discover new lands/ trade routes The Columbian Exchange • The Age of Discovery led to the migration of peoples, which in turn led to the exchange of fauna and flora – of animals, plants, and diseases, a complex process known as the Columbian Exchange. • Europeans brought wheat, grapes, olives, sugar plants, rice, bananas, horses, sheep, cattle, dogs, pigs, chicken, and goats. • Spanish & Portuguese returned to Europe with maize, white potatoes, beans, squash, pumpkins, avocados, and tomatoes. Unintended Consequences • Many things came unintentionally: • Native grasses • Diseases such as : – Small pox – Typhus – Influenza – Syphilis Columbian Exchange Led To… Global & Cultural Impact of the Columbian Exchange • Transformed economic activity • Spread of religion • Spread of Languages • Destruction of native civilizations • Spread of plants & animals • Improved diets of Asian, African, & European peoples • Spread of Smallpox and other diseases long with new weapons of war and economic exploitation, causing a massive population decline among Native Peoples. Role of Improved• Technology • In the 15th century, Portuguese invented the caravel, a small light, 3 masted sailing ship more that was more maneuverable, could carry heavy cannons, and more goods. • Magnetic compass allowed sailors to determine their position. Gunpowder, compass, and rudder all Chinese inventions! • Lateen (triangular) sail, developed by the Arabs, allowed Europeans to tack against the wind. • Astrolabe – perfected by the Arabs, used the Sun or a star to ascertain a ship’s latitude • By 1500, cartography, the art and science of map making was fairly accurate. Improved Technology Important Dates • • • • • • 1450 – 1650 Age of Discovery 1492 – Columbus lands on San Salvador 1518 – Atlantic Slave Trade Begins 1520 – Spaniards defeat the Aztec Empire 1532 – Pizarro defeats the Inca Empire 1550 –1700 Disease leads to 80% population decline in American Southeast • 1602 – Dutch East India Company established • 1635 – Tokugawa Shogunate closes Japan to trade