Colombia - Peace and Conflict Studies
advertisement
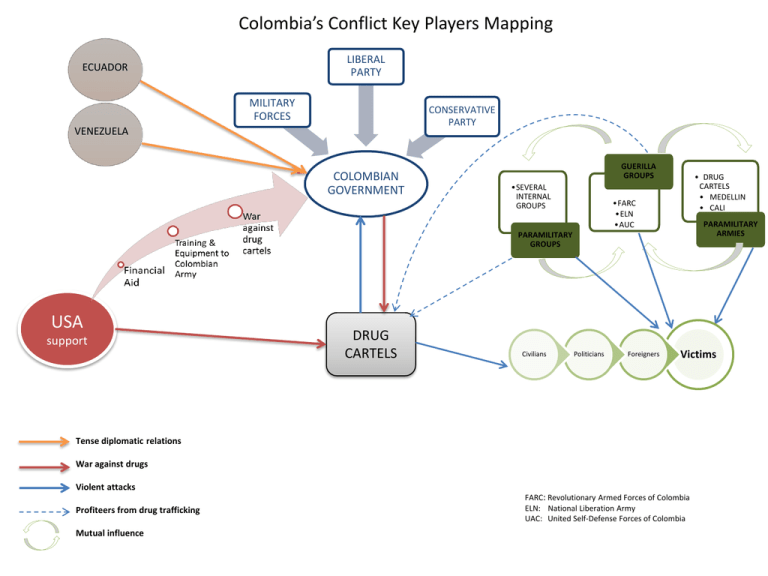
Colombia’s Conflict Key Players Mapping LIBERAL PARTY ECUADOR MILITARY FORCES CONSERVATIVE PARTY VENEZUELA COLOMBIAN GOVERNMENT GUERILLA GROUPS •SEVERAL INTERNAL GROUPS • DRUG CARTELS • MEDELLIN • CALI •FARC •ELN •AUC PARAMILITARY ARMIES PARAMILITARY GROUPS USA support DRUG CARTELS Civilians Politicians Foreigners Victims Tense diplomatic relations War against drugs Violent attacks Profiteers from drug trafficking Mutual influence FARC: Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia ELN: National Liberation Army UAC: United Self-Defense Forces of Colombia Structural and Attitudinal Factors Structural Land Inequality Social Agrarian Reform Law FARC platform Weak State Failed to provide human security, basic services Failed rule of law Human rights issues Violence Forced land displacement Shared security factors Governance/Social Capital Social Divide Intergroup Relations Guerillas & Drug Cartel Violence Forced Land Displacement Kidnappings Civil wars Social Inequality Poverty: Rural areas 63%, vs Urban areas 39% 3.9 mil IDPs Democratic Security Reform Local Town Hall Meetings Kidnappings Developing trust Military HR abuses Community partnership Social Inequality Weak Social Structure Poverty Rural 63% vs Urban 39% 3.9 mil IDPs Poverty/Inequality Power struggle between political parties Transactional Factors During Peace Talks 1998 – 2000 Pastrana •Ceased fire •Demilitarized zones prior to peace talks •Safe Haven given to FARC 2001-2002 Uribe 2004-2010 Uribe 2012-present Santos • Government stops peace talks • Uribe’s local security working groups •Demilitarization of AUC •Government and AUC begin peace talks •Peace talks with ELN in Cuba • Santos initiates secret meetings with FARC leaders • Peace talks begin in Cuba • FARC declares 2 month cease fire Columbia’s Current Peace Process FARC & Government Negotiators Land reform USA NORWAY CUBA End of armed conflict VENEZUELA OBSERVERS Agenda Key Areas Guarantees of political opposition GUARANTORS OF THE PEACE PROCESS Supporters of Colombia’s Peace Talks Rights of Victims of the conflict Drug trafficking Colombia’s Peace Talks Timeline Pastrana’s Peace Initiatives •1998 – President Andres Pastrana Arango begins peace talks with guerrillas. •1998 - Pastrana grants FARC a safe haven the size of Switzerland to help move peace talks along. •1999- President Pastrana demilitarizes vast zone to facilitate peace talks •2000 - Pastrana's "Plan Colombia" wins almost $1 billion in mainly military aid from the US to fight drug-trafficking •2001-FARC accused of using safe haven to rearm, prepare attacks and conduct drug trade. •2002- Peace process breaks down Alvaro Uribe’s Democratic Security •2003 - Fighters from rightwing AUC begin to disarm. •2004 -AUC and government begin peace talks. •2005 - 15-day dispute with Venezuela over the capture of a FARC leader on Venezuelan soil. •2005 - Exploratory peace talks with ELN, begin in Cuba. •2008 March - A Colombian cross-border strike into Ecuador kills senior FARC rebel Raul Reyes and sparks a diplomatic crisis with both Ecuador and Venezuela •2008 July - Colombian army rescues the country's highest-profile hostage, Ingrid Betancourt, held in captivity for six years by FARC President Santos’ Peace Talks •2011 May - Senate approves law to compensate victims of civil conflict and return land to millions of displaced people. •2012 August - President Santos says exploratory talks are under way with the FARC guerrillas, and that the ELN armed group has also indicated a readiness to talk. •2012 October – President Santos apologizes to indigenous leaders in Amazon region for 1912-29 killings. •2012 October Colombia and FARC negotiators launched Norway peace talks •2012 November Peace talks start in Havana, Cuba •2013 October- 15th round of talks opened in Havana, Cuba.











