Asian Cultures Unit
advertisement

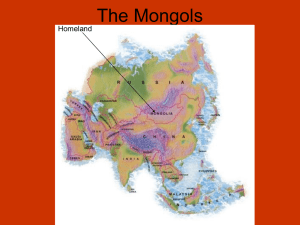
ASIAN CULTURES UNIT 350 BCE – 1400 CE China and India 350 BCE – 600 CE Defense Trade Advances East Asia 550 – 1400 Technological Advances The Mongols Status of Women in Asian Cultures Comparisons to Americas & Africa Americas: Government, Achievements, Religion Africa: Adaption to Environment, Trade & Blending of cultures China & India 350 BCE – 600 CE First Chinese Empire 221 BCE: Qin became the first unified Chinese empire LEGALISM: political philosophy taught efficient government key to maintaining order and control Qin Reforms To strengthen security, workers joined separate defensive walls in Northern China GREAT WALL OF CHINA hundreds of thousands of peasants toiled and many died Trade & Buddhism China’s most prized possession is: SILK Revealing the secret of its making was punishable by death Merchants traveling between China and Central Asia used a series of overland routes SILK ROADS: network of routes stretched from China to Mediterranean Linked China to India, Middle East, and Roman Empire Brought Buddhism to China Brought more hope to Chinese than Chinese Advances Paper – made by grinding plant fibers, like hemp, into a paste and left to dry “books” created by connecting several sheets to create scroll Iron plow and wheelbarrow Seismograph – measured earthquakes ACUPUNCTURE: inserting fine needles into skin at specific points to cure disease and relieve pain Indian Advances Hindu-Arabic Numerals: first to use the symbol for 0 Without which modern math would not be possible Numerals we use today Earth revolves around the sun Circumference of the earth Accurate to 1% View map on pages 242-243 Compare insets on Roman and Han conflicts with Nomads What effects did nomads have on the Roman empire? The Chinese empire? What was the most extensive empire between 100-400 CE? Which group of nomads traveled the farthest? East Asia 550-1400 China – Inventions & Innovations Porcelain – ceramic known as “china” Sought after around the world Woodblock Printing A page of text is carved into a block of wood Wood is coated with ink Pressed to paper THE DRAGON IS THE IMPERIAL SIGN Movable Type – individual letters or characters OF CHINA carved Rearranged and reused China – Inventions & Innovations Paper Money Facilitated Trade Trade expanded along improved roads and canals Silk Roads – routes connected china to markets in Central Asia, India and beyond! Ship Building advances led to sailing around Asia Status of Women Foot Binding: Feet tightly wrapped with pieces of cloth Restricted growth of feet so they appeared small and dainty Extremely painful Over time bones deformed Also limited movement The Mongol Empire STEPPES: grasslands, stretch across north-central Eurasia Home to nomadic people Too dry for farming Lived as pastoralists, relying on herds Traded for items they lacked Or, swept through and took what they wanted Mongols Sheep and Goat herders Skilled with horses Divided into clans Each clan led by a KHAN: CHIEF 1206: Genghis Kahn “Universal Leader” conquered rival Mongol clans and became leader of all Mongols Genghis Khan Built an Empire! Built a powerful military machine Enforced strict discipline Demanded complete loyalty Highly mobile, struck quickly Military leader Surrounded and trapped enemy Brutality Psychological warfare Burned any town that resisted Sent agents ahead to build fear of approaching forces Mongol Empire Over 20 years, Mongols conquered much of Asia Learned the art of siege warfare and gunpowder 1227: at his death, Genghis Khan controlled much of China and Central Asia Mongols divided his empire into Khanates: regions Heirs ruled each region PAX MONGOLIA: Mongols ruled peacefully, tolerated local beliefs, allowed local rulers to stay in power, created stability Japan Archipelago: large island chain Japan is the length of the eastern coast of the US Volcanic Early Japan SHINTO: everything in nature, sun, rocks, trees, animals has a spirit (kami) No sacred text or structure Build shrines to kami and perform ceremonies for blessings Shrines located in natural settings dedicated to unusual trees, waterfalls, etc Red Gateway marks the entrance to a shrine Similarities with the Americas Government Achievements Religion Government City-States throughout Mesoamerica (Mexico) formed alliances Aztecs (1100s) required conquered people to pay tribute – tax Inca (Peru) put governors throughout their conquered empire Achievements Maya and Aztecs kept written records Incans kept tax records, census, livestock records on QUIPU: knotted, colored cords Aztecs created a 365 day calendar Accurate calculations of the movements of the planets Trade & Architecture Inca Roads: paved with stone blocks, 14,000 miles, crossed every terrain imaginable (sea level to 12,000 miles high) First known suspension bridges crossed canyons and rivers Machu Pichu: as advanced as Rome Religion Inca kept mummies of dead kings and worshipped them Created temples to worship Polytheistic Ceremonies led by found 3 In 1999, Archaeologists priests preserved bodies of Inca who were sacrificed to the gods in the mountains, and preserved thanks to the dry cold. Similarities with Africa Adaption to Environment Trade & Blending of cultures Environment Large size (3xs the USA) has a wide variety of climates and vegetation Low, wide plains run across Northern and Western interior: SAHARA DESERT: LARGEST DESERT IN THE WORLD East is the Great Rift Valley, Rivers: Congo, Zambezi, Niger, Nile Outer parts have several mountain ranges Agriculture & Trade Hunter-Gatherers, to Pastoralists, to farmers As farming developed, people needed more land and spread out Women farmed, men raised cattle Islam spread to Africa through trade Iron, gold, cattle, salt, Trade led to blending of African, Arab, and Asian cultures SWAHILI: AFRICAN-ARAB