THIS IS THE ONE I WILL USE
advertisement

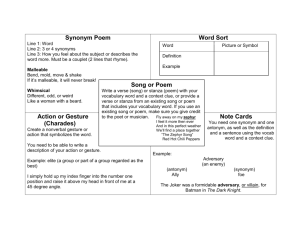
POETIC DEVICES The song does it MOOD The emotional tone, the feeling that one gets from the description of the setting. “I can feel it coming in the air tonight, Oh Lord I’ve been waiting for this moment, all my life, Oh Lord Can you feel it coming in the air tonight, Oh Lord, Oh Lord” -Phil Collins What kind of mood does these first lines give our listener? What do the opening rifts of the guitar do for the mood of the poem? STANZA The grouping of verse lines in a poem—longer than a single line. FYI: a single line of poetry is called a verse. “Do not go gentle into that good night, Old age should burn and rave at close of day; Rage, rage against the dying of the light.” --Dylan Thomas, Do not go Gentle into that Good Night” What do you notice about the lines? Its punctuation? INTERNAL RHYME The repetition of sounds in two or more words or phrases that appear in the same line of a poem. “She said it’s really not my habit to intrude Furthermore, I hope my meaning won’t be lost or misconstrued But I’ll repeat myself at the risk of being crude There must be fifty ways to leave your lover Fifty ways to leave your lover.” ONOMATOPOEIA Words whose definition comes from the sounds they make. Think Batman and the old television series. Every time there was a hit it was POW, SMACK, BAM! Flush your toilet, crack your gum, or shatter a piece of glass: the sound you hear, is another example of this poetic device. Listen in the song, what examples can your ears pick up? ASSONANCE The repetition of similar vowel sounds What is the vowel sound that you hear repeatedly during this song? The answer is? An a sound, an e sound REFRAIN A line or part of a line, a group of lines, which is repeated in the course of the poem—they can be changed slightly and they usually come at the end of the stanza. Those of us who are musicians know refrain because when we sing it is usually called the chorus or refrain. What do the Fab Four use as their refrain in this song, She Loves You? MOTIF A recurring feature which can be a name, image or phrase in a work of literature. What did the man sail to the sea? ALLITERATION ‘Tis the opposite of assonance It is the repetition in a group of words of similar consonant sounds. What is our repeated consonant sound in the song we have just heard? SYMBOL No, it is not a percussion device Look around you in this room, do you see any symbols? Something that represents something bigger than it actually is a symbol. What is our symbol in Willie Nelson’s song? (CLASSICAL) ALLUSION The author makes reference to something of literary note in his/her works, and the reader is expected to know the reference. ALLUSION Same as classical, but has one difference: the author makes reference to a historical person, place, or event in his/her literary work. CONNOTATION It is the choice of words that fit the perception of the word. What do the words “Escape” and “Pina Colada” connote for the voice in this song? METAPHOR It is the comparison of two unlike things SIMILE The comparison of two unlike things using the words like or as. PERSONIFICATION When the author gives non human things human like qualities.