Communication Barriers

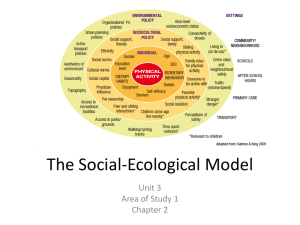
Shannon’s Communication Model
• Communication is impaired by noise factors or ‘barriers’
BSBPMG507A Manage Project Communications
Barriers to Effective Communication
1.
Language Barriers
2.
Cultural Barriers
3.
Individual Barriers
4.
Organisational Barriers
5.
Interpersonal Barriers
6.
Attitudinal Barriers
7.
Channel Barriers
BSBPMG507A Manage Project Communications
Barriers to Effective Communication
1. Language Barriers
Different languages, vocabulary, accent, dialects
Semantic gaps are words having similar pronunciation but multiple meanings – these can easily be misunderstood
Poorly expressed message, incorrect interpretation and unqualified assumptions
The use of difficult or inappropriately technical terms
2. Cultural Barriers
Can create boundaries and separate people from each other in such a way as to prevent understanding
Gender
Beauty
Economic
Position
Cultural
Background
Social Status
Education Temperament
Ethics
Age
Popularity
Motives
Assumptions
Priorities
Political
Views
Health
BSBPMG507A Manage Project Communications
Barriers to Effective Communication
3. Individual Barriers
May be a result of an individual's perceptual and personal discomfort
Even when two people have experienced the same event their mental perception may be different and acts as a barrier
Style, selective perception, halo effect, poor attention, poor retention, defensiveness, close mindedness, insufficient filtration
Can result from unrelated external forces, stress and personal change
4. Organisational Barriers
Organisational culture, values, protocols, rules, regulations, accepted norms and behaviours
Physical set up of work stations
Communication tools and working facilities
BSBPMG507A Manage Project Communications
Barriers to Effective Communication
5. Interpersonal Barriers
– Lack of knowledge of non-verbal clues like facial expression, body language, gestures, postures, eye contact
– Managers
Lack of trust in staff
Different priorities from employees
Lack of understanding of employee expectations
Authority and power imbalance
Fear of losing of control
– Staff
Lack of trust in Manager or Employer
Lack of motivation and co-operation
Fear of consequences
Information overload
BSBPMG507A Manage Project Communications
Barriers to Effective Communication
6. Attitudinal Barriers
Limitation in physical and mental ability
Differences in intellect, understanding and perceptions
Lack of trust and fear of consequences
7. Channel Barriers
Inappropriate selection of communication channel
Inappropriately structured message – eg too long, no summary, no clear outcome
Lack of access to communication media
Impacts clarity, accuracy and effectiveness
BSBPMG507A Manage Project Communications
Overcoming the Barriers - Do’s
• Allow employees access to resources, self expression and idea generation
• Express your expectations to others
• Avoid absolute words such as "never", "always", "forever
• Avoid “Yes….But”
• Be a good, attentive and active listener
• Filter the information correctly before passing on to someone else
• Establish direct communication channels
• Eliminate intermediaries
BSBPMG507A Manage Project Communications
Overcoming the Barriers - Do’s
• Maintain eye contact if culturally acceptable
• Use specific and accurate words which are easily understood
• Try and view the situations through the eyes of the speaker
• Provide summaries and key messages if information is very detailed or complicated
• Oral communication must be clear and not heavily accented
• Explain technical concepts and provide definitions
BSBPMG507A Manage Project Communications
Overcoming the Barriers - Do’s
• Ask for clarification and paraphrase to confirm understanding
• Break down hierarchies and chains of command
• Foster congenial relationships between staff and managers
• Focus on purposeful and well focused communication
• Seek and act on feedback
• Keep an open mind
BSBPMG507A Manage Project Communications
Overcoming the Barriers – Don’ts
• Be a Selective Listener - this is when a person hears another but selects not to hear what is being said or to hear a different message
• Try to “win” and score points or prove the other person wrong
• Daydream
• Use long chain of command for communication
• Use technical jargon or unusual words
• Jump to conclusions
• Interrupt the speakers and distract them by asking too many irrelevant questions
• Digress off the main topic
BSBPMG507A Manage Project Communications