CONSTITUTION NOTES
advertisement

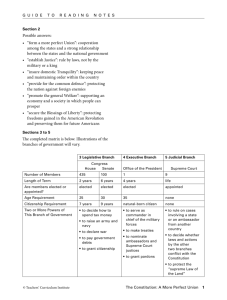
CONSTITUTION NOTES First, the basics… 7 Articles (that’s the big ideas) 27 Amendments (things that have changed over the years) • any addition to the Constitution is called an amendment • the 1st 10 amendments are called the Bill of Rights A few notable amendments: • Civil War amendments: – 13th : prohibited slavery – 14th: gave citizenship to African-Americans (also due process, equal protection clauses) – 15th – gave African American males the right to vote 17th Amendment • direct election of Senators – previously Senators had been chosen by state legislators 18th Amendment • Prohibition – only amendment to be repealed Extension of voting rights – note the groups that were not included in the original Constitution • 15th – gave African American males the right to vote • 19th – gave women the right to vote • 26th – gave 18 yr. olds the right to vote 7 basic principles included in the Constitution: 1. popular sovereignty – notion that people are the only legitimate source of power 2. representative government – people elect representatives to make political decisions 3. limited government – rule of law; gov’t may do only what citizens allow 4. separation of powers • executive – President – law-executing • legislative – Congress – law-making • judicial – courts – law-interpreting 5. checks and balances – each branch is restrained by the others examples: Congress can remove judges through impeachment Congress can override a presidential veto checks and balances continued… President can veto legislation President appoints Supreme Court justices (& other federal judges) Supreme Court can declare Presidential acts unconstitutional Supreme Court can declare acts of Congress unconstitutional 6. judicial review – courts have power to declare any gov’t action unconstitutional 7. federalism – division of authority between states and national gov’t Amending the Constitution formal changes happen 4 ways (changing written words): 1. 2/3 vote in each House + ¾ state legislatures (used most often 2. proposed by Congress + ¾ state legislatures (only used once) 3. national convention, called by Congress, requested by 2/3 states (never used) 4. proposed by national convention, ratified by ¾ state conventions Informal ways – without changing any of the written words; is the key to vitality of the Constitution 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. passage of basic legislation by Congress executive agreement – pact made by the president with head of another nation Court decisions – Woodrow Wilson said, “… a constitutional convention in continuous session.” party practices – G. Washington warned against parties; no mention of parties in Constitution custom – a. b. c. Cabinet officials – not mentioned in Constitution succession to the President – not mentioned in Constitution prior to 25th Amendment limited terms prior to 22nd Amendment The one restriction the Constitution places on the subjects with which proposed amendments may deal… • Nothing may change equal representation in the Senate. How many resolutions calling for amendments have been sent to the States, and how many have been finally ratified? • 33 sent • 27 ratified • Term to remember: extradition: to return fugitives from the law across state lines