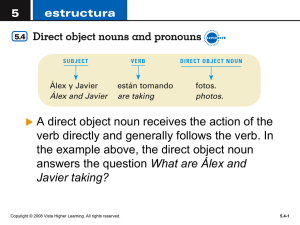
With the exception of commands, all the verb
forms you have been using have been in the
indicative mood.
The subjunctive is not a tense; rather, it is a
mood. Tense refers to when an action takes
place (past, present, future), while mood
merely reflects how the speaker feels about
the action. The subjunctive mood is rarely
used in English, but it is widely used in
Spanish.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-1
The indicative mood is used to state facts
and to express actions or states that the speaker considers
to be real and definite. It is used to express factual
information and certainty. In contrast, the subjunctive
mood expresses the speaker’s attitudes toward events,
as well as actions or states the speaker views as
uncertain or hypothetical.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-2
The difference between indicative and
subjunctive is the difference between…
– certainty/objectivity (indicative)
– possibility/subjectivity (subjunctive)
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-3
Usted va al Perú en diciembre.
No dudo que usted va al Perú en
diciembre.
Dudo que usted vaya al Perú en
diciembre.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-4
Usted tiene mucho tiempo libre.
Es verdad que usted tiene mucho tiempo
libre.
Me alegro que usted tenga tiempo libre.
Me sorprende que usted tenga tiempo
libre.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-5
Ellos son de la Republica Dominicana.
Es seguro que ellos son de la Republica
Dominicana.
Es posible que ellos sean de la Republica
Dominicana.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-6
Tengo un novio que es simpatiquísimo.
Busco a alguien que sea simpatiquísimo.
Quiero alguien que sea simpatiquísimo.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-7
Can you make an indicative statement out of the
sujunctive sentences below?
Ej. Ustedes siempre ayudan con los quehaceres.
Ej. Vamos a ayudar a preparar la comida.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-8
Segun estos ejemplos, ¿cómo crees que se forma el
subjuntivo?
Quiero que me hables a mí.
Dudo que me escribas una carta.
Es bueno que bebas agua.
Es probable que vayan a comer.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-9
The present subjunctive is formed very much
like usted and ustedes and negative tú
commands. From the yo form of the present
indicative, drop the -o ending, and replace it
with the subjunctive endings.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-10
The present subjunctive endings are:
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-11
Verbs with irregular yo forms show the same
irregularity in all forms of the present subjunctive.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-12
To maintain the -c, -g, and -z sounds, verbs
ending in -car, -gar, and -zar have a spelling
change in all forms of the present subjunctive.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-13
Present subjunctive of stem-changing verbs
-Ar and -er stem-changing verbs have the
same stem changes in the subjunctive as they
do in the present indicative.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-14
-Ir stem-changing verbs have the same stem
changes in the subjunctive as they do in the
present indicative, but in addition, the
nosotros/as and vosotros/as forms undergo a
stem change. The unstressed e changes to i,
while the unstressed o changes to u.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-15
Irregular verbs in the present subjunctive
These five verbs are irregular in the present
subjunctive.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-16
¡Atención! The subjunctive form of hay
(there is, there are) is also irregular: haya.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-17
General uses of the subjunctive
The subjunctive is mainly used to express:
1) will and influence, 2) emotion, 3) doubt, disbelief, and
denial, and 4) indefiniteness and nonexistence.
WEIRDO
– Will
– Emotion
– Impersonal expressions (what we are studying today!)
– Recommendations
– Doubt
– Ojalá
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-18
The subjunctive is most often used in
sentences that consist of a main clause and a
subordinate clause. The main clause contains a
verb or expression that triggers the use of the
subjunctive. The conjunction que connects the
subordinate clause to the main clause.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-19
These impersonal expressions are always
followed by clauses in the subjunctive:
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-20
Ejemplos…
Alyssa, quiero que le des tu lápiz a Claire.
Quiero que ustedes estén en la clase a las 9.
Zoe, quiero que vayas de compras esta
tarde.
Quiero que ustedes sepan todas las formas
del subjuntivo.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-21
Main clauses ending in que require
subjunctive in the subordinate clause.
Es importante que aprendamos español.
Es necesario que yo entienda esta lección.
Es bueno que los estudiantes traigan sus
libros.
In order to use the subjunctive in the
subordinate clause, the conjunction que
must be present and there must be a
change in subject.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-22
Es importante que limpies la cocina.
Es importante limpiar la cocina.
Why is the subjunctive only used in the first
sentence?
While the first example states one person’s
responsibility, the second is a broad
statement about the importance of cleaning
kitchens.
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
3.3-23
Indica el presente de subjuntivo de estos verbos.
Es importante que….
1. (alquilar, beber, vivir)
2. (estudiar, aprender, asistir)
3. (encontrar, poder, dormir)
4. (hacer, tener, venir)
5. (dar, hablar, escribir)
6. (pagar, empezar, buscar)
7. (ser, ir, saber)
8. (estar, dar, oír)
Copyright © 2008 Vista Higher Learning. All rights reserved.
alquile, beba, viva
que yo ______________
que tú __________
que él __________
que nosotras __________
que ellos __________
que ustedes __________
que yo __________
que tú __________
3.3-24