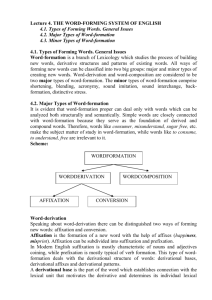
Word Formation
advertisement

Revision What allomorphic features do words have in E and U if viewed from the semasiological side? What allomorphic features do words have in E and U if viewed from the onomasiological side? What are typologically relevant types of idioms? massacre of the innocents There is no use crying over spilt milk Don't whistle until you are out of the wood. Не знаючи броду, не лізь у воду. to apply for/to accept the Chiltern Hundreds dine with Duke Huphrey mind ones p's and q's when Queen Ann was alive a pretty penny товчеться, як Марко по пеклу Word Formation Word formation processes in English and Ukrainian The lexical stock of every language is constantly growing outer means (borrowings) inner means. The lexical system of English contains about 70% of borrowed words, Ukrainian -10% An essential change of English an acceptor language => a donor language new words of English origin - 90-95%, borrowed words 5-10%. Most productive word-formation processes now are: compounding(36%), affixation (20%) new trends, pointing up in the productive field -clipping, blending and conversion, “Conversion will be more active in the future, because it is a very easy way to create new words in English” (Cannon, 1985: 415). Common word-building processes in E and U: Derivation Compounding Abbreviation Blending Back-formation (reversion) Reduplication Accentual Word-formation Semantic change Specific English types of word-formation Conversion Lexicalisation of (some) grammatical forms Derivation Derivation is generally regarded as the most productive formation process in both languages. Derivational affixes can be either prefixes or suffixes. Eng. non-re—present-ation-al-ism Укр. не-до-виторг-ув-ан-ий The allomorphism is that: E has more root morpheme words U has a richer system of derivational affixes than E E derivation is usually either suffixation or prefixation while in U prefixal-suffixal models prevail Typological classification of prefixes International antivirus - антивірус Semantically identical foresee – передбачити, postwar - післявоєнний National dedecamp mismisstate malmalnourish midmidlife попо-українському щощонайкраще попопопоїсти Typological classification of sufixes Noun suffixes Agent Abstract notions Diminutive Augmentative Compounding Another highly productive process is compounding. A compound is created by combining two or more free morphemes (often nouns). talkshow verb + noun tightrope adjective + noun overshadow preposition + noun Allomorphisms in E and U compounding : Ukr. сompounds are formed with the help of the linking interfixal element Землечерпалка, театрознавець Eng. compounds are formed through the juxtaposition of free morpheme Motherland, social-economic, sky-blue Though there a few cases of compounds with a linking element Anglo-Saxon, electro-therapy, craftsman, SinoAmerican, Afro-Asian (Cont.) In Ukr. spelling of compounds is strict while in E a great diversity of spelling is observed (dictionaries often give two variants), that is why stress is important as a marker of compounds in English. Abbreviation Clipping Partial abbreviation Blending Initialisms and acronyms Abbreviation. Clipping Shortening longer words is a popular strategy for conserving breath when speaking and space when writing or typing. Clipping is very productive in both conversational and official style. Beginning element – doc, prof, mayo (mayonnaise) Final element – phone, copter, vator (elevator) Omitting of beg. and final element simaltaneously fridge, flue In Ukr. such words can be used only within compound words генпрокуратура, міськрада Abbreviation. Partial abbreviation. Partial abbreviation is found in both languages modem (modulator-demodulator), hi-fi (high fidelity), fro-yo ( frozen jogurt) yнівермаг, держдеп (державний департамент) In translating they are usually transformed into word phrases (cont.) Abbreviation. Blending Blends are combinations of two or more words in which the sound patterns overlap. Often parts of either or both words are reduced or lost in the blend, though usually the initial components are still recognizable. brunch = breakfast + lunch, motel = motor + hotel, smog = smoke + fog, Oxbridge=Oxford+Cambridge, Wenglish (Welsh + English) Аскофен (аспірін+кофеїн) New blends : vodkatini = vodka + martini (vodka cocktail) wintertainment = winter + entertainment Japanimation = Japan + animation spork = spoon + fork spooktacular events – Halloween events Halloweek – a week of scary events Cocacolonization = Coca Cola + colonization Product names: Gogurt = go +yogurt (‘portable yogurt’) Craisins = cranberry + raisins (‘dried cranberies’) Dijonaise = Dijon + mayonnaise Initialisms and acronyms Other forms of shortenings are initialisms (also called alphabetisms)and acronyms, which reduce each component word to its initial letter. The difference between the two types lies in how the resulting lexeme is pronounced in spoken language. Initialism - a set of letters pronounced as such and standing for an idea, group, or institution (BBC, for British Broadcasting Corporation) Initialisms: TV, CD, MP3, MP, CNN, UFO, BYOB - Bring your own beverages/bottle TGIFT Укр. США, МВФ, НБУ Specifically English – initial abreviation and complete word combined A-life (artificial life in computers), U-language (upper class English) Acronym a set of letters pronounced as a word (NATO, pronounced ‘Nay-toe’, for North Atlantic Treaty Organization SCUBA Self-contained underwater breathing apparatus AIDS Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome UNESCO; BBL, bf, u2, BRB, Hand Укр. СНІД, СОТ, ДАІ The newest: ELF - English as Lingua Franca Back-formation Sometimes speakers of a language will analyze a word as containing affixes where none are present. By removing these assumed affixes a lexeme can be back-formed. Editor - to edit, babysitter - to babysit This word-formation process can be approached only diachronically Examples: editor (1649) edit (1791) television (1907) televise (1927) Paramedical (1921) paramedic (1967 Укр. Галасувати =>галас, говорити =>говір Specific English types of wordformation Conversion Lexicalisation of (some) grammatical forms Conversion a word class change without any morphological marking party (noun) -> party (verb) We will be at the party They like to party must (verb) -> must (noun) You must eat your soup It is a must that you call him open (A, V, N) right (A, V, N, Adv) round (A, V, N, Adv, Prep) Conversion models from N to V: to pepper,to shape,to fuel, to ship from V to N: fear, laugh, judge from Adj to V: to open, to black, to quiet from a closed category (functionals) to notionals: ‘ifs' , 'buts' from phrase compounds to Adj.: down-to-earth language from phrase compounds to V: dog and pony show - to dog and pony, to have a green thumb - to green thumb, to give a green light - to green light a blue pencil to blue-pencil Lexicalisation of (some) plural forms Look up these words in the dictionary Air - airs (UC pl) Minute - minutes (UC pl) Picture - pictures (UC pl) Damage - damages (UC pl) Add some more on the list Revise independently: Affixation E and U prefixes E and U suffixes Reduplication Accentual Word-formation Semantic change Mizin T.O. LECTURES IN CONTRASTIVE LEXICOLOGY OF THE ENGLISH AND UKRAINIAN LANGUAGES. – Kyiv, 2005. Мизин Т.О. Курс лекцій з порівняльної лексикології англійської та української мов. Навчальний посібник для студентів III курсу факультету лінгвістики. – Київ, 2005.