If would have
advertisement

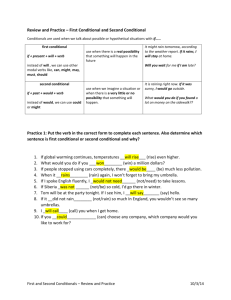
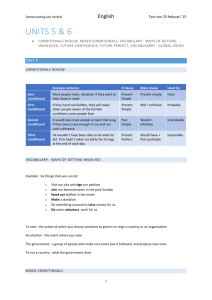
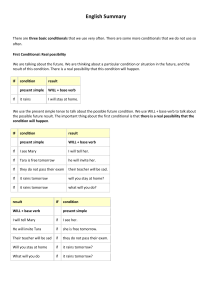
There are three basic conditionals that we use very often. There are some more conditionals that we do not use so often. First Conditional Second Conditional Third Conditional The structure of conditional • First Conditional If future simple (will + vb-base form) + subj + present simple, subj Unless may/might + base form imperative • Second Conditional If would + subj + past simple, subj + vb- base form Unless could/might • Third Conditional If would have + subj + past perfect, subj + participle Unless could/might have First conditional • This expresses what will happen if the condition indicated. EJ: If I finish the project soon, I will go to the cinema with you. • We can use modal May and Might or the verb in the imperative. EJ: If the library is open, I may / might borrow a book If the senteces are negative To deny the verb of the condition To use it in conjunction with affirmative unless (if not) EJ: He won´t believe anything unless we prove it is true Second conditional • The conditional concernes the present but it’s hypothetical, in other words, it’s almost impossible to occur. EJ: If you told him, he would understand the situation. • If the verb TO BE appears, in all persons we must use WERE. EJ: If that camera weren´t so expensive, I would buy it. • When we give an advice, we must use the pronoun WERE, instead of I. EJ: If I were you, I would ask my parents for permission Third conditional • In this case the sentences also express a condition in the past and the hypothesis can’t be possible. EJ: You would have learnt to play the guitar sooner If you had taken classes • The variants to form the third condiconal are perfect manners. Could have + participle Might have + participle EJ: If we had bought the tickets on time, we could / might have gone to the cinema Prayer time The same structure as the first conditional conjunctions change EJ: When I get home, I´ll call you EJ: I will buy a car as soon as I pass my driving test The structure of Wishful Wish / if only + past simple Wish / if only +past perfect Wish + could / would + base form wishful prayers expressed a desire, can be formed in two ways: Past simple • In this tense situations we refer a present situatio that we would change. EJ: I wish / If only I were more responsible • If the verb TO BE appears, in all persons we must use WERE. EJ: I wish / If only it were that simple! Past perfect • In this situation we refer to a past situation that we had wanted to change. EJ: I wish / If onlyearlier! Could or Would • In this time we refer to a future situation expressing the hope that this situations will happen. EJ: I wish / I could pass the literature test • If the subject of "whish" and the verb in base form are different, we use "would" EJ: I wish / If only the weather would improve Match the beginning of each sentence in I to a suitable ending in II. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Jim wishes I’d be delighted If he hadn’t been poor, If he finishes his homework, Let us know If he goes to Scotoland, She would have been pleased ...... a. ...... b. ...... c. ...... d. ...... e. ...... f. ...... g. if you had apologised. he may visit a castle. life would have been easier. he had more free time. if you lived nearer. he can watch television. if you want to come. Rewrite the sentences using the words in brackets. 1.-She should have listened to the doctor. (if only) If only she had listened to the doctor. ………………………………………. 2.-We didn’t meet you because we didn’t know the train time. (if) If we had known the train time, we would have ………………………………………………… met you. ………… 3.-Sam always has to rush because he gets up late. (earlier) If………………………………………………… Sam got up earlier, he wouldn’t have to rush.