Chapter 5 Key Issue 2
advertisement

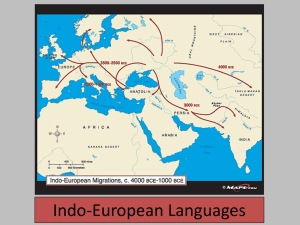
Chapter 5 Key Issue 2 Germanic Branch West Germanic group- subgroups named for what? High-German Low- English, Dutch, Flemish North Germanic group Swedish, Danish, Norwegian, Icelandic All 4 derive from Old Norse Became 4 different languages- why? Indo-Iranian Branch Indic (Eastern) group India + neighbors Major language of this group- Hindi Why is Hindi considered one singular language, even though there are many ways to speak it? Hindi not the official language of India- why? Repercussions of this? Iranian (Western) group Iran + neighbors Languages include Persian and Kurdish What alphabet are these languages written in? Balto-Slavic Branch Slavic was once a single language- why did differences develop? East Slavic and Baltic groups Russian is by far the most primarily spoken of this group- why? Other languages in this group are Ukrainian and Belarusian West and South Slavic groups Polish, Czech, and Slovak are most widely spoken in this group Czechoslovakia language difficulties? Serbo-Croatian has become what? Bosnian, Croatian, Serbian What is the main difference between the Bosnian/Croatian version and the Montenegran/Serbian version of Serbo-Croatian? What are some other differences? Romance Branch Romance branch evolved from which language? Four languages correspond to the boundaries of which four countries? Four languages: Four countries: Diffusion of English- Case Study Celts- British Isles, 2000 BC Invasion- Germanic tribes, 450 AD Anglo-Saxons Normans- 1066 AD French only Most people kept speaking English- why? Combination words = English America- 1607 England defeated France in battle for colonization in 1700s Colonies- 1600s-1899 Ireland, South Asia, South Pacific, southern Africa, Philippines Diffusion of Romance Languages- Case Study Latin- “Roman’s language” Roman Empire- spread Latin through __ diffusion? Latin in the captured provinces- “Vulgar Latin”, which was the people’s Latin After the Roman Empire collapsed, these different regions’ versions of Latin changed because of __? Diffusion of Proto-Indo-European: Theory 1 Proto-Indo-European: the original language that the Indo-European *family* evolved from (the roots of our tree) Theory 1: The Nomadic Warrior Hypothesis Marija Gimbutas is the author of this hypothesis First PIE speakers were the Kurgan people Lived between Russia and Kazakhstan Can be traced back to 4300 BC Conquered much of Europe and South Asia, spread PIE as they went Diffusion of Proto-Indo-European: Theory 2 Theory 2: The Sedentary Farmer Hypothesis Supporters of this theory include Colin Renfrew and Russell D. Gray First PIE speakers lived in Turkey about 2000 years or more before the Kurgans They migrated west and northwest This all occurred through peaceful migrationbecause the speakers were agricultural, their culture and language triumphed What does agriculture have to do with it? Understanding Check Describe the diffusion of either English, Romance languages, or one of the theories of the Proto-IndoEuropean language One paragraph May use notes Four Indo-European Branches Germanic (1 group) Indo-Iranian Indic/Eastern (1 group) Iranian/Western (1 group) Balto-Slavic East Slavic and Baltic (1 group) West and South Slavic (1 group) Romance (1 group) Diffusion of English (1 group) Diffusion of Romance (1 group) Diffusion of Indo-European #1 (1 group) Diffusion of Indo-European #2 (1 group)