Indo-European Language Branch
advertisement

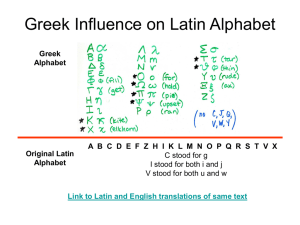
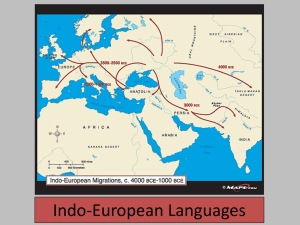
Indo-European Language Family Why is English related to Other Languages? English = Indo-European language family A language family- a collection of langs related thru a common ancestor that existed long before recorded history. Indo-European is the language family with the most speakers (~3 bil). Indo-European Branches W/in lang families are language branches A language branch- a collection of langs related thru a common ancestor that existed thousands of years ago. differences are not as extensive/old as with lang. families archaeological evidence can confirm that the branches derived from the same family Indo-European is divided into 8 branches: Germanic, Romance, Balto-Slavic, Indo-Iranian, Greek, Albanian, Celtic, and Armenian Diagram the Branches On the paper provided, create a diagram/hierarchy of Indo-European family tree Be sure to include all the languages on the handout provided. Include information about # of speakers (if impt) and where it will be spoken. You may want to note which are official languages or have various alphabets Outline the origin & diffusion section on the back/ own paper Germanic Branch English = Germanic Language Branch West Germanic Group A language group is a collection of langs w/in a branch that share a common origin in the relatively recent past, & display relatively few differences in grammar and vocab West Germanic Group Includes the languages of German & English, Afrikaans, and Dutch High Sub-Group: German is spoken mainly in Germany, Austria, and Switzerland Low Sub-Group: English is spoken on every continent (key places: Great Britain, United States, Canada, India, Japan, and Australia) Dutch in the Netherlands, Flemish in Belgium Afrikaans in South Africa & Namibia (like Dutch) North Germanic Group Sometimes called Nordic North Germanic languages of Swedish, Norwegian, Icelandic, and Danish Derived from Old Norse English word Icelandic word apple epli book bók high/hair hár house hús mother móðir night nótt stone steinn that það word orð S c Romance Branch The Romance Branch evolved from the Latin lang. spoken by Romans 2,000 years ago The four most common Romance languages are Spanish, Portuguese, French, and Italian French and Spanish are two of the six official UN languages Romance Branch Romanian in Romania and Moldova Others include Romansh (one of Switzerland’s 4 official languages), and Catalan (spoken in Spain, and the official language of Andorra) Only one spatially separated 4 more in Europe Haiti: French Creole is ex. of Rom. language spoken outside Eur. Creole creolized language = mix of a colonial language and an indigenous lang Forms when a colonized grp adopts the lang of the dominant grp, but makes some changes (usually involving vocab from native lang or grammar changes) History of the Romance Languages Latin was spread by the soldiers of the Roman Empire When they conquered a group of people, they taught them Latin The ppl spoke a different form of Latin called Vulgar Latin, or Latin of the People. Ex: The Latin word for horse is equus, but the Vulgar Latin word for horse was caballus. Italian: cavallor, Spanish: caballo, Portuguese: cavalo, and French: cheval Spanish and Portuguese Both of these languages are important around the world due to Spanish and Portuguese imperialism Spanish is the official language in 18 Latin American countries Lingua franca of region Portuguese is the official language of Brazil Balto-Slavic Branch Roots are more Asian Due to isolation of different groups when they arrived in Eastern Europe, different languages emerged East*, West, South Slavic and Baltic GROUP Languages include: Ukrainian, Russian, Czech, Slovak, Polish, Serbo-Croatian, Bulgarian, and the Baltic langs Balto-Slavic Branch Russian is most widely spoken lang, and is spoken by 80% of the Russians Russian is one of the 6 official languages of the UN Russification post-WWII Ukrainian and Belarusian next in # for East Slavic. The Eastern Baltic languages include Latvian and Lithuanian. Balto-Slavic Branch Main West Slavic languages are Polish (Poland), Czech and Slovak (former Czechoslovakia) Speakers of Czech and Slovak can understand each other South Slavic- Slovene in Slovenia, Macedonian in Macedonia, and SerboCroatian is spoken by rest of Yugo. w/ conflicts, similarities are NOT being preserved Montenegrans & Serbs use Cyrillic alphabet Indo-Iranian Branch The Indo-Iranian branch has the most speakers. It has over 100 langs with over 1 billion native speakers The branch includes the languages of Persian (Farsi), Bengali, Hindi, Urdu, and Punjabi The Indic (eastern) Group 1/3 of Indians use Hindi Spoken many different ways, but there is 1 common written form of the language called Devanagari India’s constitution recognizes 18 official languages 4 diff lang. families present The Indic (Eastern) Group Pakistan’s principal language is Urdu, and the written form is Arabic alphabet Bangladesh’s main language is Bengali English not official. Only 1% speak it But often common language, de facto lang. The Iranian (Western) Group Indo-Iranian languages are spoken in Iran and neighboring countries Persian, or Farsi, is main lang in Iran. Other languages include Kurdish and Pashto (Pathan/Pashtun) All of these are written w/ Arabic alphabet. Other Languages Greek, Albanian, Celtic, and Armenian are in the Indo-European family, but stand on their own Greek: in Greece, 12 million native speakers. Armenian: in Armenia, 6 million native speakers. Albanian: in Albania (some Serbia, Italy), 7.3 million native speakers Celtic: in UK (some France), 1.4 million Ex: Gaelic, Welsh, Cornish Gimbutas: war Renfrew: agriculture