The Language Tree - Culture--per6

An crann teanga
L'arbre des langues
De taal boom kalbos medis
Drzewo języka
The Language Tree
What is the Language tree?
The language tree is not really a tree, it’s a chart that they have made to look like a tree and it shows how each language is connected to the other.
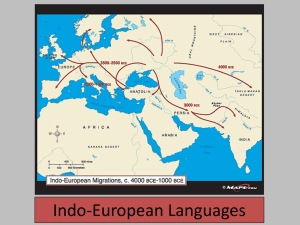
This tree shows indo-European branches and the four main groups of languages in the indo
European culture which are the
Anatolian, the Celto–Italo-Tocharian, the Balto-Slavo
Germanic, and Aryano–Greco–Armenic. All these are at the trunk of the tree, they branch off into nine language groups all together. These groups consist of Anatolian, Celtic, Romance,
Germanic, Baltic, Slavonic, Iranian, Indic, and Greek.
In the Anatolian ….
Anatolian
The Anatolian branch of the Indo-
European language tree consist of five languages; Hittite,
Palaic, Lydian,
Luwian, and Lycian.
In the Celto–Italo-Tocharian…
The Celtic language branch consist of two inner branches; the
Brittanic and Gaulish.
On the Brittanic branch there are three languages; Cornish,
Breton, and Welsh.
On the Gaulish branch there are three languages as well which include
Scottish, Irish, and
Manx.
Celtic
The Romance language consist of four languages;
Romanian,
Spanish,
French, and
Italian.
Romance
In the Balto-Slavo
Germanic…
Germanic
The Germanic branch of the language tree has two sub branches within. One is called the Western
Germanic branch, and the other is called the
Scandinavian branch. The
Western Germanic branch consist of six languages;
Flemish, Dutch, Low
German, High German,
Frisian, and English. The
Scandinavian branch consists of four languages;
Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Norwegian.
The Baltic branch of the language tree consist of three languages; Old
Prussian,
Lithuanian, and
Latvia.
Baltic
The Slavonic branch of the language tree consist of three sub branches;
Southern Slavic, Proto –
Russian, and Western
Slavic. In the Southern
Slavic branch, there are three languages; Serbo-
Croatian, Bulgarian, and
Slovenia. In the Proto –
Russian branch there are three languages;
Ukrainian, White Russian, and Great Russian. In the
Western Slavic branch there are two languages;
Polish and Czech.
Slavonic
In the Aryano–Greco–Armenic …
The Iranian branch of the language tree consist of three languages;
Persian, Pashto, and Baluchi.
Iranian
The Indic branch of the Language tree consist of five languages;
Hindi, Marathi,
Gujarati, Panjabi, and Bengali.
Indic
In the Greek branch of the language tree there are four languages ;
Arcadian,
Aeolic, Ionic, and Doric.
Greek
All the stuff in between
In addition to the nine language branches; there are several small sub groups in between such as Osco
– Umbrian, Gothic, Armenian, and Tocharian.
The Osco – Umbrian branch is connected to the
Italic branch, which connects to the Latin branch which connects to the Romance branch of the tree. The Gothic branch connects to the
Scandinavian branch of the tree. The Armenian is a branch off the Armeno – Aryan branch, and the
Tocharian branch is connected to the Celto –
Italo- Tocharian branch.
To sum it all up?
Each of these languages are connected to each other in at least one way, they are all Indo –
European languages, meaning they are all a family coming from the same hearth.
Small part within the tree…
The big picture…
Indo –
European
Part
This is the whole tree with every known language placed and organized within to show how each and every language is related to one another through the “Mother
Tongue”.