File - Mrs. Atcheson
advertisement

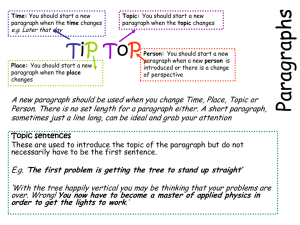
Show what you know . . . All sentences contain two basic elements- a subject and a verb. The subject answers the questions Who? or What? before the verb. The verb tells what the subject does, what is done to the subject, or the subject’s condition. S V Example: Jackie runs. A simple sentence contains 1 independent clause. It also contains a subject and a verb. Example: [This book is good] independent clause A compound sentence consists of 2 or more independent clauses. Compound sentences are joined by a comma and a coordinating conjunction (FANBOYS). Example: [This book is good] , and [I will finish it today.] A complex sentence contains one independent clause and one or more subordinate clauses. A subordinate clause contains a subject and a verb, but cannot stand alone (example: If I go,) subordinate clause Example: (If I finish this book,) [I will bring it to you.] independent clause A compound-complex sentence consists of 2 or more independent clauses and one or more subordinate clause. subordinate clause independent clause Example: (If I bring it to you,) [I will let you borrow it] ,but [I am afraid of not getting it back.] independent clause Determine the sentence structure of the following sentences. As soon as I got the letter, I read the instructions, and I knew that I wanted to go. * compound-complex 2. Have you found the map? * simple 3. This situation is confusing, but I hope to have clarification soon. * compound 4. If I visit the county fair, I will buy a funnel cake. * complex 1. Declarative- states an idea and ends with a period Carrollton has a population of 24,000. Interrogative- asks a question and ends with a question mark What do you expect to learn? Imperative- gives an order or a directions; ends with a period or an exclamation mark Clean your room, now! Turn to chapter 26. Exclamatory- Conveys a strong emotion and ends with an exclamation mark This stinks! A noun is a person, place, thing, or idea. There are 4 types: • Compound- two nouns put together to make one ex. football, ice age, father-in-law • Common- person, place, thing, idea, or concept • Proper- specific name of a noun ex. Mrs. Atcheson,Georgia • Collective- one word/noun to represent a group ex. team, flock James Patterson is easily one of my favorite authors. ◦ proper A company of dancers will entertain us first. ◦ collective The library at Carrollton Junior High will close at 4:00 p.m. ◦ common To do well at our game, we will need a lot of teamwork. ◦ compound A pronoun takes the place/replaces a noun. Antecedent – word the pronoun takes the place of in the sentence Kinds of Pronouns ◦ Personal- refer to the person speaking, the person spoken to, or thing spoken about ◦ Demonstrative- point out a specific noun this, that, these, those ◦ Relative-begins a subordinate clause that, which, who, whom, whose ◦ Interrogative- begins a question what, which, who, whom, whose ◦ Indefinite – not specific Mr. Phillips accepted his award with dignity. ◦ 3rd person personal That is the last piece of cake! ◦ Demonstrative No one really knows that Mrs. Ogles has magic powers. ◦ Indefinite Mrs. Allen is the person who is in charge today. ◦ Relative Who knows how old Dr. Simpson is? ◦ Interrogative A verb shows action. ◦ Visible or mental Linking Verbs- connects a noun or pronoun at or near the beginning of a sentence with a word at or near the end. Helping Verbs- added before another verb ◦ Help create a verb phrase She felt sick after she ate rotten bananas. ◦ linking Her mother felt her head to see if she had a temperature. ◦ action They had felt for splinters in the stray cat’s foot. ◦ helping Adjectives answer these 4 questions: What kind? white fence Which one? this photo How many? two snacks How much? enough time Answers 1 of 4 questions: ◦ Where? jogged here ◦ When? arrive tonight ◦ In what manner? smiled happily ◦ To what extent? hardly know She tearfully accepted the award. ◦ tearfully He has never asked for much help. ◦ never My science teacher is a very friendly person. ◦ very I jog weekly. ◦ weekly Last Saturday, I thoroughly cleaned our bathrooms. ◦ thoroughly We live close to the school. ◦ close Prepositions relates the noun or pronoun following it to another word in the sentence. A Prepositional Phrase BEGINS with a preposition and ENDS with an Object of Preposition. 3 Types . . . ◦ Coordinating F A N B O Y S May look for comma before in some cases ◦ Correlative ◦ Subordinating Begins a subordinate clause (has subject and verb, but is dependent) May look for comma before in some cases She not only won first prize, but she also went on to the regional competition. ◦ correlative Please go to the store and then straight home. Will Zeke or Kendall be going with us? Whether you like it or not, you will clean your room! ◦ coordinating ◦ coordinating ◦ correlative Neither Grandma nor Grandpa can drive anymore. ◦ correlative Expresses feeling and emotion ◦ Some types of emotion that might be shown . . . Surprise Joy Pain Impatience Hesitation Anger Functions independently from the rest of the sentence and is set off from the rest of the sentence with an exclamation mark or a comma. Ouch! I caught my finger in the door. ◦ pain Wow! I am so excited you are here. ◦ joy Hey! I have told you not to do that! ◦ anger Yuck! I don’t like that at all. ◦ dislike Whew! I am so glad that meeting is over. ◦ relief