Conditional Sentences
advertisement

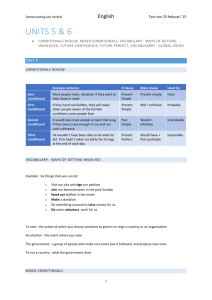
Conditional Sentences The meaning of Conditional Sentences Conditionals Factual Future (predictive) Imaginative (Subjunctive) 1. Timeless •Generic •Habitual 1. Strong condition and result 1. Hypothetical • Present • Future 2. Time-bound •Implicit inference •Explicit inference 2. Degrees of weakened condition or result 2. Counterfactual • Present • Past Factual Conditional Sentences Generic Factual Conditionals Relationships that are true and unchanging • If oil is mixed with water, it floats. • If you boil water, it vaporizes. Normally take a simple present tense in both clauses. Especially frequent in scientific writing. Factual Conditional Sentences Habitual Factual Conditionals Relationship based on habit; Past or present relationships that are habitually true. • If I wash the dishes, Sally dries them. • If Nancy said, “Jump!” Bob jumped. Both clauses usually have the same tense Frequent in conversation. Factual Conditional Sentences Implicit inference conditionals Specific time-bound relationships. Much wider range of verb tenses. • If smog can be licked in L.A., it can be licked anywhere. • If the radicals haven’t made the government more responsive, they have wasted their time. • If there was a happy man in the world that night, it was John Tunney. Both clauses usually have the same tense “When(ever)” cannot substitute for “if”. Factual Conditional Sentences Explicit inference conditionals Specific time-bound relationships. Marked with modals. • If he was there, he must have seen the painting. Usually makes use of “must” or “should”. “When(ever)” cannot substitute for “if”. Future Conditional Sentences Strong Condition or Result Future plans or contingencies; Normal pattern is simple present tense in the if clause and some explicit indication of future time in the result clause. • If it rains, I’ll stay home. • If you finish your vegetables, I’m going to buy you an ice cream cone. • If Steve comes to class, he will get the answers to the quiz. Future Conditional Sentences Degrees Prediction scale – Result Clause: • • • • of Weakened Conditional or Result will, be going to = should = may = might = certain (strong result) probable possible (stronger than might) possible (weaker than may) To weaken the condition clause: • should; happens to; should happen to Imaginative Conditional Sentences Hypothetical Conditionals Express what the speaker perceives to be unlikely yet possible events or states in the if clause; Can refer to the future as well as the present • If Joe had the time, he would go to Mexico. (Present) • If Joe were to have the time, he would go to Mexico. (Future) The if clause is not strongly negated. Imaginative Conditional Sentences Hypothetical Conditionals The negative quality of the if clause can be even further weakened so that the possibility of the result occurring becomes stronger: • If Joe should have the time, he would go to Mexico. • If Joe happened to have the time, he would go... • If Joe should happen to have the time, he would go... Imaginative Conditional Sentences Hypothetical Conditionals Sometimes, the difference between using a future conditional and a hypothetical conditional is a matter of speaker choice: • If it rains, I’ll stay home. (Future) • If it were to rain, I would stay home. (Hypothetical) Imaginative Conditional Sentences Counterfactual Conditionals Express impossible events or states in the if clause Reference to the present or past • If my grandfather were alive today, he would experience a very different world. (Present) • If my grandfather had been alive in 1996, he would have been 100 years old. (Past) The if clause is strongly negated.